Potential of platinum-resensitization by Wnt signaling modulators as treatment approach for epithelial ovarian cancer
- PMID: 32681294
- PMCID: PMC7467966
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-020-03317-4
Potential of platinum-resensitization by Wnt signaling modulators as treatment approach for epithelial ovarian cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Canonical Wnt/ β-catenin pathway is one mechanism being activated in platinum-resistant epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). Detecting potential targets for Wnt pathway modulation as a putative future therapeutic approach was the aim of this study.
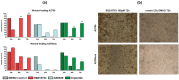
Methods: Biological effects of different Wnt modulators (SB216763, XAV939 and triptolide) on the EOC cell lines A2780 and its platinum-resistant clone A2780cis were investigated via multiple functional tests. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was carried out to compare the expression levels of Wnt marker proteins (β-catenin, snail/ slug, E-cadherin) in patient specimens and to correlate them with lifetime data.
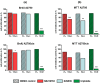
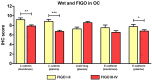
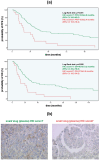
Results: We could show that activated Wnt signaling of the platinum-resistant EOC cell line A2780cis can be reversed by Wnt manipulators through SB216763 or XAV939. All Wnt manipulators tested consecutively decreased cell proliferation and cell viability. Apoptosis of A2780 and A2780cis was enhanced by triptolide in a dose-dependent manner, whereas cell migration was inhibited by SB216763 and triptolide. IHC analyses elucidated significantly different expression patterns for Wnt markers in the serous subtype. Herein, higher plasmatic snail/ slug expression is associated with improved progression-free (PFS) and overall survival (OS).
Conclusion: According to the described effects on EOC biology, all three Wnt manipulators seem to have the potential to augment the impact of a platinum-based chemotherapy in EOC. This is promising as a dominance of this pathway was confirmed in serous histology.
Keywords: E-cadherin; Ovarian cancer; Platinum-resistance; Snail/ slug; Wnt; β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
Sven Mahner reports grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca, Clovis, Medac, MSD, PharmaMar, Roche, Sensor Kinesis, Tesaro and Teva outside the submitted work. Fabian Trillsch has received grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca, Clovis, Medac, PharmaMar, Roche and Tesaro outside the submitted work. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Anglesio MS, Wiegand KC, Melnyk N, Chow C, Salamanca C, Prentice LM, Senz J, Yang W, Spillman MA, Cochrane DR, Shumansky K, Shah SP, Kalloger SE, Huntsman DG (2013) Type-specific cell line models for type-specific ovarian cancer research. PLoS ONE 8:e72162. 10.1371/journal.pone.0072162 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arend RC, Londoño-Joshi AI, Straughn JM Jr, Buchsbaum DJ (2013) The Wnt/β-catenin pathway in ovarian cancer: A review. Gynecol Oncol 131:772–779. 10.1016/j.ygyno.2013.09.034 - PubMed
-
- Baldwin LA, Hoff JT, Lefringhouse J, Zhang M, Jia C, Liu Z, Erfani S, Jin H, Xu M, She Q-B, van Nagell JR, Wang C, Chen L, Plattner R, Kaetzel DM, Luo J, Lu M, West D, Liu C, Ueland FR, Drapkin R, Zhou BP, Yang XH (2014) CD151-α3β1 integrin complexes suppress ovarian tumor growth by repressing slug-mediated EMT and canonical Wnt signaling. Oncotarget 5:12203–12217. 10.18632/oncotarget.2622 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barghout SH, Zepeda N, Xu Z, Steed H, Lee C-H, Fu Y (2015) Elevated β-catenin activity contributes to carboplatin resistance in A2780cp ovarian cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 468:173–178. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.10.138 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

