Evaluation of adherence to pediatric status epilepticus management guidelines in Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 32683397
- PMCID: PMC8015475
- DOI: 10.17712/nsj.2020.3.20190106
Evaluation of adherence to pediatric status epilepticus management guidelines in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Objective: To assess compliance with the 2017 Saudi pediatric status epilepticus management guidelines and to printout the main obstacle for adherence to the guidelines.
Methods: A cross sectional study conducted in September 2019, using electronic survey. The survey sent to all the Pediatric Emergency physicians practicing in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) through emails and WhatsApp and the questionnaire based on clinical scenario written in English language.
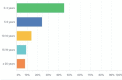
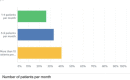
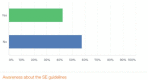
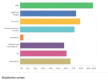
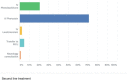
Results: One hundred and three (70%) of 147 physicians working in KSA and covering pediatric emergency departments responded to the survey. Only 20% of the physicians reported full compliance to all 4 guideline components; 57% reported that they were not aware of the published guidelines.
Conclusion: Pediatric emergency physicians reported poor compliance to the 2017 published guidelines for the treatment of children with convulsive status epilepticus in KSA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Management of convulsive status epilepticus in children: an adapted clinical practice guideline for pediatricians in Saudi Arabia.Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2017 Apr;22(2):146-155. doi: 10.17712/nsj.2017.2.20170093. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2017. PMID: 28416791 Free PMC article.
-
Adherence to surviving sepsis guidelines among pediatric intensivists. A national survey.Saudi Med J. 2017 Jun;38(6):609-615. doi: 10.15537/smj.2017.6.17737. Saudi Med J. 2017. PMID: 28578440 Free PMC article.
-
Brazilian pediatricians' adherence to food allergy guidelines-A cross-sectional study.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 24;15(2):e0229356. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229356. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32092100 Free PMC article.
-
COPD care in Saudi Arabia: physicians' awareness and knowledge of guidelines and barriers to implementation.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2017 May 1;21(5):592-595. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.16.0656. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2017. PMID: 28399976
-
Questionnaires used to assess barriers of clinical guideline use among physicians are not comprehensive, reliable, or valid: a scoping review.J Clin Epidemiol. 2017 Jun;86:25-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2016.12.012. Epub 2017 Jan 17. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017. PMID: 28104462
Cited by
-
Survey of Pediatric Status Epilepticus Treatment Practices and Adherence to Management Guidelines (Pedi-SPECTRUM e-Survey).Indian J Crit Care Med. 2024 May;28(5):504-510. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24707. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 38738206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pujar SS, Martinos MM, Cortina-Borja M, Chong WKK, De Haan M, Gillberg C, et al. Long-term prognosis after childhood convulsive status epilepticus: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2018;2:103–111. - PubMed
-
- Gurcharran K, Grinspan ZM. The burden of pediatric status epilepticus: Epidemiology, morbidity, mortality, and costs. Seizure. 2019;68:3–8. - PubMed
-
- Al-Shamy S, Hosny AO, Ismail MT, Alsekaya MS, Abdeldayem M. Evaluation of Adherence to The Neurocritical Care Society Guidelines in Management of Generalized Convulsive Status Epilepticus at The Emergency Department of Suez Canal University Hospital. Journal of Neurological Disorders. 2018;06:3–5.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
