What does a hemogram say to us?
- PMID: 32684755
- PMCID: PMC7344121
- DOI: 10.14744/TurkPediatriArs.2019.76301
What does a hemogram say to us?
Abstract
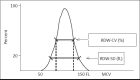
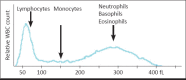
The most commonly performed blood test is complete blood cell count. This test includes hemoglobin, white blood cell count, platelet count, and detailed red blood cell indices. Automated complete blood count also give information for "differential" which gives information about percentages and absolute numbers of different subgroups of white blood cells. This test is necessary in diagnosing anemia, hematological cancers, infections, acute hemorrhagic states, allergies, and immunodeficiencies. Also it is used for monitoring side effects of certain drugs. A pediatrician is frequently challenged for evaluating complete blood count as a part patient's assessment. An enhanced and complete understanding of this laboratory test is essential for providing quality care of sick and normal children. Here in this paper, we want to share key laboratory interpretation strategies for complete blood count and some clues for differentiating normal from deviations and true problems.
En sık istenilen kan testi tam kan sayımıdır. Bu test hemoglobin, lökosit, trombosit sayılarını ve ayrıntılı olarak eritrosit parametrelerini içerir. Otomotik kan sayım cihazlarının verdiği sonuçlar artık lökosit alt gruplarının yüzdeleri ve sayıları konusunda da bilgi vermektedir. Kan sayımı; anemi, hematolojik kanserler, enfeksiyonlar, akut kanamalar, alerjik hastalıklar ve immün yetmezliklerin tanısı için gerekli bir testtir. Ayrıca bazı ilaçların yan etkilerinin izlemi için de gereklidir. Bir çocuk hekiminin hastasını değerlendirmesi genelde tam kan sayımı okumasını ve yorumlamasını da gerektirir. Bu testin nitelikli olarak değerlendirilmesi hasta ve normal çocuk izleminde önemlidir. Bu yazıda hemogram değerlendirmesinde önemli noktalara değinilerek normal ve sorunlu durumların ayrılabilmesi için ipuçları paylaşılmıştır.
Keywords: Abnormal hemogram values; child; hemogram; normal hemogram values.
Copyright: © 2020 Turkish Archives of Pediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The author have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures








References
-
- Bennett ST, Lehman CM, Rodgers GM. 2nd ed. Heidelberg: Springer; 2015. Laboratory hemostasis; pp. 68–108.
-
- Loscalzo J, Schafer AI. 3rd ed. Lippincott Williams-Wilkins; 2003. Thrombosis and Hemorrhage; pp. 315–30.
-
- Beutler E, Lichtman MA, Coller BS, Kipps TJ, Seligsohn U. 6th ed. McGraw Hill; 2001. Hematology; p. 1471.
-
- Jacobs DS, DeMott WR, Oxley DK. 5th ed. Lexi-Comp; 2001. Laboratory Test Handbook; pp. 326–58.
-
- Desai SP, Isa-Pratt S. 2nd ed. Lexi-Comp; 2002. Clinician's guide to Laboratory Medicine:A Practical Approach.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

