Apoptosis related microRNAs and MGMT in glioblastoma cell lines submitted to treatments with ionizing radiation and temozolomide
- PMID: 32684859
- PMCID: PMC7358627
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rpor.2020.06.007
Apoptosis related microRNAs and MGMT in glioblastoma cell lines submitted to treatments with ionizing radiation and temozolomide
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the effect of radiotherapy and temozolomide on the expression of miRNAs apoptotic (miRNAs-21, -221, -222 (anti-apoptotic) and miRNAs-15a, -16 (pro-apoptotic)) and the gene MGMT in glioblastoma cell lines.
Background: The limited knowledge of the molecular biology of malignant gliomas may hinder the development of therapeutic modalities. In this scenario, one of the greatest advances of recent years was the identification of microRNAs. These molecules have an important role in biological processes involving cancer, including glioblastoma.
Materials and methods: Trypan blue was used to verify the cell viability, and real time PCR to quantify the expression of microRNAs and gene 24, 48 and 120 h after exposure to treatments.
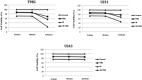
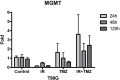
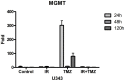
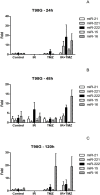
Results: There was a statistically significant decrease of expression of miR-15a between 48 and 120 h in line T98 G treated with radiation, increased expression of miR-15a between 24 and 120 h in line U251 treated with radiation and temozolomide, and increased expression of miR-16 between 24 and 120 h in line U251 treated with radiation alone and when combined with temozolomide. There was a decrease in MGMT gene expression, between 24 and 48 h in U343 cells treated with temozolomide.
Conclusions: Ionizing radiation and temozolomide modified the expression of miRNAs studied and MGMT.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Glioblastoma; Ionizing radiation; microRNAs.
© 2020 Greater Poland Cancer Centre. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Kleihues P., Sobin L.H. World Health Organization classification of tumors. Cancer. 2000;88(12):2887. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

