Treatment of infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy with RT001: A di-deuterated ethyl ester of linoleic acid: Report of two cases
- PMID: 32685351
- PMCID: PMC7358664
- DOI: 10.1002/jmd2.12116
Treatment of infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy with RT001: A di-deuterated ethyl ester of linoleic acid: Report of two cases
Abstract
Background: Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy (INAD) is a rare, autosomal recessive disease due to defects in PLA2G6 and is associated with lipid peroxidation. RT001 is a di-deuterated form of linoleic acid that protects lipids from oxidative damage.
Methods: We evaluated the pharmacokinetics (PK), safety, and effectiveness of RT001 in two subjects with INAD (subject 1: 34 months; subject 2: 10 months). After screening and baseline evaluations, subjects received 1.8 g of RT001 BD. PK analysis and clinical evaluations were made periodically.
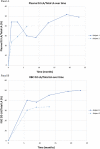
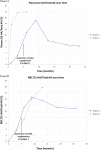
Main findings: Plasma levels of deuterated linoleic acid (D2-LA), deuterated arachidonic acid (D2-AA), D2-LA to total LA, and D2-AA to total AA ratios were measured. The targeted plasma D2-LA ratio (>20%) was achieved by month 1 and maintained throughout the study. RBC AA-ratios were 0.11 and 0.18 at 6 months for subjects 1 and 2; respectively. No treatment-related adverse events occurred. Limited slowing of disease progression and some return of lost developmental milestones were seen.
Conclusions: Oral RT001 was administered safely in two subjects with INAD. Early findings suggest that the compound was well tolerated, metabolized and incorporated in the RBC membrane. A clinical trial is underway to assess efficacy.
Keywords: INAD; NBIA; PLA2G6; PLAN; neurodegeneration.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of SSIEM.
Conflict of interest statement
D. A., J. D., and C. F. declare no conflict of interest. P. M., F. H., M. M., P. A., and M. S., are employed by and holds stock in Retrotope. R. M. is a founder and holds stock in Retrotope, Inc. Sarah Endemann is employed by Retrotope. All authors confirm that the content of the article has not been influenced by the sponsor.
Figures

References
-
- Aicardi J, Castelein P. Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy. Brain. 1979;102:727‐748. - PubMed
-
- Nardocci N, Zorzi G, Farina L, et al. Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy: clinical spectrum and diagnostic criteria. Neurology. 1999;52:1472‐1478. - PubMed
-
- Kurian MA, Morgan NV, MacPherson L, et al. Phenotypic spectrum of neurodegeneration associated with mutations in the PLA2G6 gene (PLAN). Neurology. 2008;70:1623‐1629. - PubMed
-
- Kurian MA, McNeill A, Lin JP, et al. Childhood disorders of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2011;53:394‐404. - PubMed
-
- Iodice A, Spagnoli C, Salerno GG, et al. Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy and PLA2G6‐ associated neurodegeneration: an update for the diagnosis. Brain Dev. 2017;39:93‐100. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

