Recurrent nasopharyngeal rhinosporidiosis: Case report from Qatar and review of the literature
- PMID: 32685372
- PMCID: PMC7355714
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idcr.2020.e00901
Recurrent nasopharyngeal rhinosporidiosis: Case report from Qatar and review of the literature
Abstract
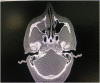
Rhinosporidiosis is a chronic granulomatous infectious disease that predominantly affects the mucosal membranes of the nose and nasopharynx. The disease is caused by Rhinosporidium seeberi, an eukaryotic pathogen with distinct geographical distribution particularly in tropical and subtropical areas acquired mainly through aquatic exposure. We report a case of a young Nepalese male who presented with recurrent right nasopharyngeal mass where surgical excision and histopathological examination confirmed the diagnosis following distinct pathognomonic findings. There is no optimal effective management of the disease and surgical excision coupled with cauterization to prevent recurrence is the recommended best option since medical treatment alone is ineffective. The clinical presentation, assessment and management options are reviewed.
Keywords: Dapsone; Mucosal polyps; Qatar; Rhinosporidiosis.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declared no competing interests in relation to current publication.
Figures

References
-
- Arseculeratne S.N. Rhinosporidiosis: what is the cause? Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2005;18(2):113–118. - PubMed
-
- Singh C.A., Sakthivel P. Rhinosporidiosis. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(14):1359. - PubMed
-
- Capoor M.R., Khanna G., Rajni Batra K., Nair D., Venkatchalam V.P. Rhinosporidiosis in Delhi, north India: case series from a non-endemic area and mini-review. Mycopathologia. 2009;168(2):89–94. - PubMed
-
- Mendoza L., Vilela R., Rosa P.S., Fernandes Belone A.F. Lacazia loboi and Rhinosporidium seeberi: a genomic perspective. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2005;22(4):213–216. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

