Relationship between Poaceae pollen and Phl p 5 allergen concentrations and the impact of weather variables and air pollutants on their levels in the atmosphere
- PMID: 32685736
- PMCID: PMC7355991
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04421
Relationship between Poaceae pollen and Phl p 5 allergen concentrations and the impact of weather variables and air pollutants on their levels in the atmosphere
Abstract
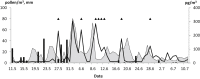
The sensitization to grass pollen is a known problem in European countries. Phl p 5 is an important allergen recognized by the majority of grass sensitized individuals. In this study, we evaluated daily variation in airborne Poaceae pollen and Phl p 5 allergen concentrations to determine whether airborne pollen concentrations alone are sufficient to reflect the actual allergenic potential of the air. The relationships between the mentioned pollen and allergen concentrations and associated environmental variables were also examined. The airborne particles were collected during the Poaceae flowering season in Bratislava in 2019. Pollen sampling was performed using a Hirst-type sampler, while a cyclone sampler was used for the aeroallergen capturing. Allergenic molecules were quantified by ELISA assay. The associations between pollen and allergen concentrations showed that these two variables are positively correlated; however, the correlation was not significant. We observed the concurrent occurrence of airborne pollen and allergen peaks on the same day. Nevertheless, during some days of the pollen season, the allergen concentrations did not correspond to the airborne pollen values. Moreover, the days with low pollen concentration but high pollen potency and vice versa were observed. The effect of selected environmental variables on daily pollen and allergen concentrations was evaluated through Spearman's correlation analysis. Of all meteorological variables considered, air temperature, precipitation, and relative air humidity were significantly correlated with airborne pollen and/or allergen concentrations. The association with air temperature was positive, while the negative association was observed with precipitation and relative air humidity. Among the atmospheric pollutants, O3 and PM10 were significantly and positively associated with both pollen and allergen concentrations, whereas CO and PM2.5 were significantly and positively associated only with pollen concentration.
Keywords: Aeroallergens; Atmospheric pollutants; Atmospheric science; Bratislava; Central Europe; Environmental analysis; Environmental health; Environmental pollution; Environmental science; Grass pollen; Meteorological parameters; Microbiology.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Atmospheric pollutants and their association with olive and grass aeroallergen concentrations in Córdoba (Spain).Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Dec;27(36):45447-45459. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10422-x. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32789634 Free PMC article.
-
Seasonal variation in the allergenic potency of airborne grass pollen in Bratislava (Slovakia) urban environment.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Nov;28(44):62583-62592. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-15179-5. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34212332 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of environmental drivers on allergy to pollen grains in a case study in Spain (Madrid): meteorological factors, pollutants, and airborne concentration of aeroallergens.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Oct;28(38):53614-53628. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-14346-y. Epub 2021 May 25. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34032952
-
Effect of meteorological parameters on Poaceae pollen in the atmosphere of Tetouan (NW Morocco).Int J Biometeorol. 2013 Mar;57(2):197-205. doi: 10.1007/s00484-012-0566-2. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Int J Biometeorol. 2013. PMID: 22744802 Review.
-
Outdoor airborne allergens: Characterization, behavior and monitoring in Europe.Sci Total Environ. 2023 Dec 20;905:167042. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167042. Epub 2023 Sep 12. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 37709071 Review.
Cited by
-
Short-Term Exposure of Dactylis glomerata Pollen to Atmospheric Gaseous Pollutants Is Related to an Increase in IgE Binding in Patients with Grass Pollen Allergies.Plants (Basel). 2022 Dec 23;12(1):76. doi: 10.3390/plants12010076. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36616204 Free PMC article.
-
Atmospheric pollutants and their association with olive and grass aeroallergen concentrations in Córdoba (Spain).Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Dec;27(36):45447-45459. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10422-x. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32789634 Free PMC article.
-
A prospective study evaluating the correlation between local weather conditions, pollen counts and pruritus of dogs with atopic dermatitis.Vet Dermatol. 2024 Oct;35(5):500-507. doi: 10.1111/vde.13268. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Vet Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38887962 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of allergen components and identification of bioactivity of HSP70 in pollen of Populus deltoides.Proteome Sci. 2021 Sep 3;19(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12953-021-00178-8. Proteome Sci. 2021. PMID: 34479544 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of environmental and community features with radiologic sinus inflammation in Pennsylvania, USA.Environ Epidemiol. 2025 Apr 29;9(3):e387. doi: 10.1097/EE9.0000000000000387. eCollection 2025 Jun. Environ Epidemiol. 2025. PMID: 40308349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aalberse E.C. Clinically significant cross-reactivities among allergens. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1992;99:261–264. - PubMed
-
- Acar A., Alan Ş., Kaplan A., Baysal E.Ö., Doğan C., Pinar N.M. General trends in atmospheric pollen concentration in the high populated city of Ancara, Turkey. Karaelmas Fen Ve Mühendis Derg. 2017;7:40–46.
-
- Adhikari A., Reponen T., Grinshpun S.A., Martuzevicius D., LeMasters L. Correlation of ambient inhalable bioaerosols with particulate matter and ozone: a two-year study. Environ. Pollut. 2006;140:16–28. - PubMed
-
- Aina R., Asero R., Ghiani A., Marconi G., Albertini E., Citterio S. Exposure to cadmium-contaminated soils increases allergenicity of Poa annua L. pollen. Allergy. 2010;65:1313–1321. - PubMed
-
- Alan Ş., Şahin A.A., Sarişahin T., Şahin S., Kaplan A., Pinar N.M. The effect of geographical and climatic properties on grass pollen and Phl p 5 allergen release. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2018;62:1325–1337. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

