Prospective Study in 355 Patients With Suspected COVID-19 Infection: Value of Cough, Subjective Hyposmia, and Hypogeusia
- PMID: 32686164
- PMCID: PMC7404620
- DOI: 10.1002/lary.28999
Prospective Study in 355 Patients With Suspected COVID-19 Infection: Value of Cough, Subjective Hyposmia, and Hypogeusia
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the incidence of certain symptoms in a population of health workers exposed to coronavirus disease 2019 patients.
Study design: Case-control study.
Methods: The study was conducted at a tertiary care hospital from March 1 to April 7, 2020. Health workers with suspected coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection were included. The presence of COVID-19 was detected by using real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) methods. Positive and negative RT-PCR patients were used as case and control groups, respectively. This study analyzed the incidence of COVID-19 symptoms in both patient groups. Visual analog scales were used for self-assessment of smell and taste disorders, ranging from 0 (no perception) to 10 (excellent perception).
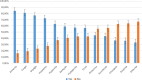
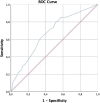
Results: There were 215 (60.6%) patients with positive RT-PCR and 140 (39.4%) patients with negative RT-PCR. The presence of symptoms such as hyposmia hypogeusia, dysthermia, and cough were strongly associated with a positive RT-PCR. The association of cough and subjective hyposmia had 5.46 times higher odds of having a positive test. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis showed that a fever higher than 37.45°C resulted in sensitivity and specificity of 0.65 and 0.61, respectively. A total of 138 cases (64.1%) and 114 cases (53%) had subjective hyposmia and hypogeusia, respectively. The 85.4% of these patients recovered olfactory function within the first 14 days of the onset of the symptoms.
Conclusion: There is a significant association between positive RT-PCR and subjective hyposmia. The association of subjective hyposmia and cough increase significantly the odds of having a positive RT-PCR. The measurement of fever as the only method for screening of COVID-19 infection resulted in a poor association.
Level of evidence: 3 Laryngoscope, 130:2674-2679, 2020.
Keywords: Hyposmia, hypogeusia, COVID-19, odds ratio, incidence, ROC.
© 2020 American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society Inc, The Triological Society and American Laryngological Association (ALA).
Figures
References
-
- Sim MR. The COVID‐19 pandemic: major risks to healthcare and other workers on the front line. Occup Environ Med 2020;77:281–282. - PubMed
-
- Rubino S, Kelvin N, Bermejo‐Martin JF, Kelvin D. As COVID‐19 cases, deaths and fatality rates surge in Italy, underlying causes require investigation. J Infect Dev Ctries 2020;14:265–267. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

