The emerging role of fibroblast-like synoviocytes-mediated synovitis in osteoarthritis: An update
- PMID: 32686306
- PMCID: PMC7520283
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.15669
The emerging role of fibroblast-like synoviocytes-mediated synovitis in osteoarthritis: An update
Abstract
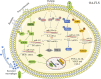
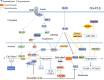
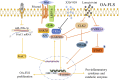
Osteoarthritis (OA), the most ubiquitous degenerative disease affecting the entire joint, is characterized by cartilage degradation and synovial inflammation. Although the pathogenesis of OA remains poorly understood, synovial inflammation is known to play an important role in OA development. However, studies on OA pathophysiology have focused more on cartilage degeneration and osteophytes, rather than on the inflamed and thickened synovium. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) produce a series of pro-inflammatory regulators, such as inflammatory cytokines, nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2 ). These regulators are positively associated with the clinical symptoms of OA, such as inflammatory pain, joint swelling and disease development. A better understanding of the inflammatory immune response in OA-FLS could provide a novel approach to comprehensive treatment strategies for OA. Here, we have summarized recently published literatures referring to epigenetic modifications, activated signalling pathways and inflammation-associated factors that are involved in OA-FLS-mediated inflammation. In addition, the current related clinical trials and future perspectives were also summarized.
Keywords: clinical trials; epigenetics; fibroblast-like synoviocytes; osteoarthritis; synovitis.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
No new data generated.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cadherin-11 involves in synovitis and increases the migratory and invasive capacity of fibroblast-like synoviocytes of osteoarthritis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 May;26(1):153-61. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.03.024. Epub 2015 Mar 28. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25824718
-
Metabolic reprogramming of synovial fibroblasts in osteoarthritis by inhibition of pathologically overexpressed pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases.Metab Eng. 2022 Jul;72:116-132. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2022.03.006. Epub 2022 Mar 13. Metab Eng. 2022. PMID: 35296430
-
Identification of Novel Genes in Osteoarthritic Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes Using Next-Generation Sequencing and Bioinformatics Approaches.Int J Med Sci. 2019 Jul 21;16(8):1057-1071. doi: 10.7150/ijms.35611. eCollection 2019. Int J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31523167 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of fibroblast-like synoviocyte transformation by transcription factors in arthritic diseases.Biochem Pharmacol. 2019 Jul;165:145-151. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.03.018. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30878552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: Role in synovial fibrosis associated with osteoarthritis.Wound Repair Regen. 2021 Jul;29(4):642-649. doi: 10.1111/wrr.12939. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Wound Repair Regen. 2021. PMID: 34021514 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the Anti-Inflammatory, Analgesic, and Chondroprotective Effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino in Osteoarthritis: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 4;25(17):9594. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179594. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273553 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Effects of Reynoutria japonica Houtt. on Pain and Cartilage Breakdown in Osteoarthritis Based on Its Multifaceted Anti-Inflammatory Activity: An In Vivo and In Vitro Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 3;25(19):10647. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910647. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408977 Free PMC article.
-
Is the Synovium the First Responder to Posttraumatic Knee Joint Stress? The Molecular Pathogenesis of Traumatic Cartilage Degeneration.Cartilage. 2023 Dec;14(4):473-481. doi: 10.1177/19476035231155630. Epub 2023 Feb 17. Cartilage. 2023. PMID: 36799236 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes treating osteoarthritis: hope with challenge.Heliyon. 2023 Jan 21;9(1):e13152. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13152. eCollection 2023 Jan. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36711315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphological and Mechanical Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles and Parent Human Synoviocytes under Physiological and Inflammatory Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 30;23(21):13201. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113201. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361990 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hou CH, Fong YC, Tang CH. HMGB‐1 induces IL‐6 production in human synovial fibroblasts through c‐Src, Akt and NF‐kappaB pathways. J Cell Physiol. 2011;226:2006‐2015. - PubMed
-
- Jansen H, Meffert RH, Birkenfeld F, Petersen W, Pufe T. Detection of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in moderate osteoarthritis in a rabbit model. Ann Anat. 2012;194:452‐456. - PubMed
-
- Zhang W, Moskowitz RW, Nuki G, et al. OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis, Part II: OARSI evidence‐based, expert consensus guidelines. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16:137‐162. - PubMed
-
- Jevsevar DS. Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: evidence‐based guideline. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2013;21:571‐576. - PubMed
-
- Wang T, He C. Pro‐inflammatory cytokines: the link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018;44:38‐50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

