Nanopore sequencing and the Shasta toolkit enable efficient de novo assembly of eleven human genomes
- PMID: 32686750
- PMCID: PMC7483855
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-020-0503-6
Nanopore sequencing and the Shasta toolkit enable efficient de novo assembly of eleven human genomes
Abstract
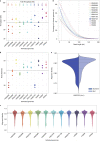
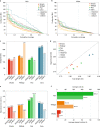
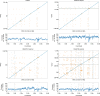
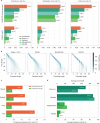
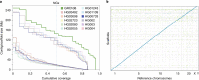
De novo assembly of a human genome using nanopore long-read sequences has been reported, but it used more than 150,000 CPU hours and weeks of wall-clock time. To enable rapid human genome assembly, we present Shasta, a de novo long-read assembler, and polishing algorithms named MarginPolish and HELEN. Using a single PromethION nanopore sequencer and our toolkit, we assembled 11 highly contiguous human genomes de novo in 9 d. We achieved roughly 63× coverage, 42-kb read N50 values and 6.5× coverage in reads >100 kb using three flow cells per sample. Shasta produced a complete haploid human genome assembly in under 6 h on a single commercial compute node. MarginPolish and HELEN polished haploid assemblies to more than 99.9% identity (Phred quality score QV = 30) with nanopore reads alone. Addition of proximity-ligation sequencing enabled near chromosome-level scaffolds for all 11 genomes. We compare our assembly performance to existing methods for diploid, haploid and trio-binned human samples and report superior accuracy and speed.
Conflict of interest statement
M.A. is a paid consultant to ONT. V.C. and S.M. are employees of ONT.
Figures




References
-
- Poplin R, et al. A universal snp and small-indel variant caller using deep neural networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018;36:983–987. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 HG010961/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL137183/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U41 HG010972/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- U41 HG007234/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG008345/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG010329/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG010971/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG010053/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG009737/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG010485/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG007990/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HG009084/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HG009730/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- OT3 HL142481/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R44 GM134994/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026682/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HG010262/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R43 HG009859/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

