The NK cell-cancer cycle: advances and new challenges in NK cell-based immunotherapies
- PMID: 32690952
- PMCID: PMC8406687
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-020-0728-z
The NK cell-cancer cycle: advances and new challenges in NK cell-based immunotherapies
Abstract
Natural killer (NK) cells belong to the innate immune system and contribute to protecting the host through killing of infected, foreign, stressed or transformed cells. Additionally, via cellular cross-talk, NK cells orchestrate antitumor immune responses. Hence, significant efforts have been undertaken to exploit the therapeutic properties of NK cells in cancer. Current strategies in preclinical and clinical development include adoptive transfer therapies, direct stimulation, recruitment of NK cells into the tumor microenvironment (TME), blockade of inhibitory receptors that limit NK cell functions, and therapeutic modulation of the TME to enhance antitumor NK cell function. In this Review, we introduce the NK cell-cancer cycle to highlight recent advances in NK cell biology and to discuss the progress and problems of NK cell-based cancer immunotherapies.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement
T. Bald has research agreements with ENA Therapeutics and Bristol Myers Squibb and is on the scientific advisory board of Oncomyx. M.F. Krummel is a founder and shareholder of Pionyr Immunotherapeutics and has research agreements with Bristol Myers Squib, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Amgen, Abbvie and Genentech. M.J. Smyth has research agreements with Bristol Myers Squibb and Tizona Therapeutics and is on the scientific advisory board of Tizona Therapeutics and Compass Therapeutics. K.C. Barry declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
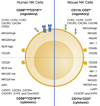
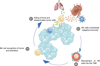


References
-
- Vivier E et al. Innate Lymphoid Cells: 10 Years On. Cell 174, 1054–1066 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Chiossone L, Dumas PY, Vienne M & Vivier E Natural killer cells and other innate lymphoid cells in cancer. Nat Rev Immunol 18, 671–688 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Soto A, Gonzalez S, Smyth MJ & Galluzzi L Control of Metastasis by NK Cells. Cancer Cell 32, 135–154 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

