Efficient hepatic delivery and protein expression enabled by optimized mRNA and ionizable lipid nanoparticle
- PMID: 32691013
- PMCID: PMC7355334
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.07.003
Efficient hepatic delivery and protein expression enabled by optimized mRNA and ionizable lipid nanoparticle
Abstract
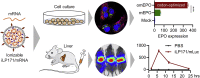
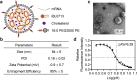
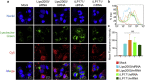
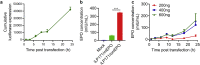
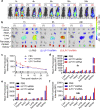
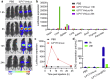
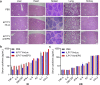
mRNA is a novel class of therapeutic modality that holds great promise in vaccination, protein replacement therapy, cancer immunotherapy, immune cell engineering etc. However, optimization of mRNA molecules and efficient in vivo delivery are quite important but challenging for its broad application. Here we present an ionizable lipid nanoparticle (iLNP) based on iBL0713 lipid for in vitro and in vivo expression of desired proteins using codon-optimized mRNAs. mRNAs encoding luciferase or erythropoietin (EPO) were prepared by in vitro transcription and formulated with proposed iLNP, to form iLP171/mRNA formulations. It was revealed that both luciferase and EPO proteins were successfully expressed by human hepatocellular carcinoma cells and hepatocytes. The maximum amount of protein expression was found at 6 h post-administration. The expression efficiency of EPO with codon-optimized mRNA was significantly higher than that of unoptimized mRNA. Moreover, no toxicity or immunogenicity was observed for these mRNA formulations. Therefore, our study provides a useful and promising platform for mRNA therapeutic development.
Keywords: Codon optimization; Erythropoietin; Lipid nanoparticle; mRNA delivery; mRNA therapy.
© 2020 [The Author/The Authors].
Conflict of interest statement
Z. L. is the founder of Suzhou Ribo Life Science Co. Ltd. The other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Hajj K.A., Whitehead K.A. Tools for translation: non-viral materials for therapeutic mRNA delivery. Nat Rev Mater. 2017;2:17056.
-
- Sahin U., Kariko K., Tureci O. mRNA-based therapeutics--developing a new class of drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014;13:759–780. - PubMed
-
- Weng Y., Li C., Yang T., Hu B., Zhang M., Guo S., Xiao H., Liang X.J., Huang Y. The challenge and prospect of mRNA therapeutics landscape. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020;40:107534. - PubMed
-
- Geall A.J., Verma A Fau - Otten G.R., Otten Gr Fau - Shaw C.A., Shaw Ca Fau - Hekele A., Fau - Banerjee K.Hekele A., Banerjee K Fau - Cu Y., Fau - Beard C.W.Cu Y., Beard Cw Fau - Brito L.A., Brito La Fau - Krucker T., Krucker T Fau - O'Hagan D.T., O'Hagan Dt Fau - Singh M., Singh M Fau - Mason P.W., Mason Pw Fau - Valiante N.M., Valiante Nm Fau - Dormitzer P.R., Dormitzer Pr Fau - Barnett S.W., Barnett Sw Fau - Rappuoli R., Rappuoli R Fau - Ulmer J.B., Ulmer Jb Fau - Mandl C.W., Mandl C.W. Nonviral delivery of self-amplifying RNA vaccines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2012;109:14604–14609. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

