Associations between COVID-19 related media consumption and symptoms of anxiety, depression and COVID-19 related fear in the general population in Germany
- PMID: 32691135
- PMCID: PMC7371788
- DOI: 10.1007/s00406-020-01171-6
Associations between COVID-19 related media consumption and symptoms of anxiety, depression and COVID-19 related fear in the general population in Germany
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Associations between COVID-19 related media consumption and symptoms of anxiety, depression and COVID-19 related fear in the general population in Germany.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2021 Oct;271(7):1409. doi: 10.1007/s00406-021-01290-8. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34272977 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
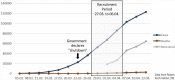
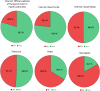
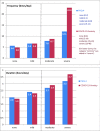
In context of the current COVID-19 pandemic the consumption of pandemic-related media coverage may be an important factor that is associated with anxiety and psychological distress. Aim of the study was to examine those associations in the general population in Germany. 6233 participants took part in an online-survey (March 27th-April 6th, 2020), which included demographic information and media exploitation in terms of duration, frequency and types of media. Symptoms of depression, unspecific anxiety and COVID-19 related anxiety were ascertained with standardized questionnaires. Frequency, duration and diversity of media exposure were positively associated with more symptoms of depression and unspecific and COVID-19 specific anxiety. We obtained the critical threshold of seven times per day and 2.5 h of media exposure to mark the difference between mild and moderate symptoms of (un)specific anxiety and depression. Particularly the usage of social media was associated with more pronounced psychological strain. Participants with pre-existing fears seem to be particularly vulnerable for mental distress related to more immoderate media consumption. Our findings provide some evidence for problematical associations of COVID-19 related media exposure with psychological strain and could serve as an orientation for recommendations-especially with regard to the thresholds of critical media usage.
Keywords: Corona; Media coverage; Mental health; Pandemic; Psychological distress; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Petzold MB, Plag J, Ströhle A. COVID-19-Pandemie—Psychische Belastungen können reduziert werden. Deutsches Ärzteblatt. 2020;117(13):648–654.
-
- Keramarou M, Cottrell S, Evans MR, et al. Two waves of pandemic influenza A(H1N1) 2009 in Wales—the possible impact of media coverage on consultation rates, April–December 2009. Euro Surveill Bull Eur sur les Maladies Transm Eur Commun Dis Bull. 2011;16(3):19772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

