Whole-Brain Map of Long-Range Monosynaptic Inputs to Different Cell Types in the Amygdala of the Mouse
- PMID: 32691225
- PMCID: PMC7674542
- DOI: 10.1007/s12264-020-00545-z
Whole-Brain Map of Long-Range Monosynaptic Inputs to Different Cell Types in the Amygdala of the Mouse
Abstract
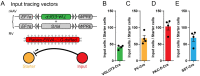
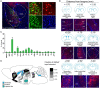
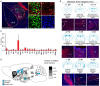
The amygdala, which is involved in various behaviors and emotions, is reported to connect with the whole brain. However, the long-range inputs of distinct cell types have not yet been defined. Here, we used a retrograde trans-synaptic rabies virus to generate a whole-brain map of inputs to the main cell types in the mouse amygdala. We identified 37 individual regions that projected to neurons expressing vesicular glutamate transporter 2, 78 regions to parvalbumin-expressing neurons, 104 regions to neurons expressing protein kinase C-δ, and 89 regions to somatostatin-expressing neurons. The amygdala received massive projections from the isocortex and striatum. Several nuclei, such as the caudate-putamen and the CA1 field of the hippocampus, exhibited input preferences to different cell types in the amygdala. Notably, we identified several novel input areas, including the substantia innominata and zona incerta. These findings provide anatomical evidence to help understand the precise connections and diverse functions of the amygdala.
Keywords: Basolateral amygdala; Central amygdala; GABAergic; Glutamatergic; Mouse; Rabies virus retrograde tracing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Baxter MG, Murray EA. The amygdala and reward. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:563–573. - PubMed
-
- Douglass AM, Kucukdereli H, Ponserre M, Markovic M, Grundemann J, Strobel C, et al. Central amygdala circuits modulate food consumption through a positive-valence mechanism. Nat Neurosci. 2017;20:1384–1394. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

