SARS-CoV-2 Entry Receptor ACE2 Is Expressed on Very Small CD45- Precursors of Hematopoietic and Endothelial Cells and in Response to Virus Spike Protein Activates the Nlrp3 Inflammasome
- PMID: 32691370
- PMCID: PMC7370872
- DOI: 10.1007/s12015-020-10010-z
SARS-CoV-2 Entry Receptor ACE2 Is Expressed on Very Small CD45- Precursors of Hematopoietic and Endothelial Cells and in Response to Virus Spike Protein Activates the Nlrp3 Inflammasome
Abstract
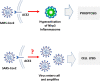
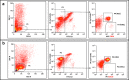
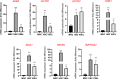
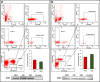
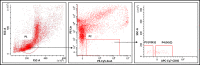
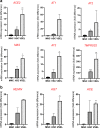
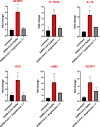
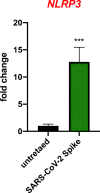
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) plays an important role as a member of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) in regulating the conversion of angiotensin II (Ang II) into angiotensin (1-7) (Ang [1-7]). But at the same time, while expressed on the surface of human cells, ACE2 is the entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2. Expression of this receptor has been described in several types of cells, including hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs), which raises a concern that the virus may infect and damage the stem cell compartment. We demonstrate for the first time that ACE2 and the entry-facilitating transmembrane protease TMPRSS2 are expressed on very small CD133+CD34+Lin-CD45- cells in human umbilical cord blood (UCB), which can be specified into functional HSCs and EPCs. The existence of these cells known as very small embryonic-like stem cells (VSELs) has been confirmed by several laboratories, and some of them may correspond to putative postnatal hemangioblasts. Moreover, we demonstrate for the first time that, in human VSELs and HSCs, the interaction of the ACE2 receptor with the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein activates the Nlrp3 inflammasome, which if hyperactivated may lead to cell death by pyroptosis. Based on this finding, there is a possibility that human VSELs residing in adult tissues could be damaged by SARS-CoV-2, with remote effects on tissue/organ regeneration. We also report that ACE2 is expressed on the surface of murine bone marrow-derived VSELs and HSCs, although it is known that murine cells are not infected by SARS-CoV-2. Finally, human and murine VSELs express several RAAS genes, which sheds new light on the role of these genes in the specification of early-development stem cells. Graphical Abstract •Human VSELs and HSCs express ACE2 receptor for SARS-CoV2 entry. •Interaction of viral spike protein with ACE2 receptor may hyperactivate Nlrp3 inflammasome which induces cell death by pyroptosis. •SARS-CoV2 may also enter cells and eliminate them by cell lysis. •What is not shown since these cells express also Ang II receptor they may hyperactivate Nlrp3 inflammasome in response to Ang II which may induce pyroptosis. Our data indicates that Ang 1-7 may have a protective effect.
Keywords: ACE2; COVID19; Cytokine storm; Hematopoietic stem cells; Nlrp3 inflammasome; Pyroptosis; SARS-CoV-2; Spike protein; VSELs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human Hematopoietic Stem, Progenitor, and Immune Cells Respond Ex Vivo to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021 Feb;17(1):253-265. doi: 10.1007/s12015-020-10056-z. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021. PMID: 33089452 Free PMC article.
-
Distinctive Roles of Furin and TMPRSS2 in SARS-CoV-2 Infectivity.J Virol. 2022 Apr 27;96(8):e0012822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00128-22. Epub 2022 Mar 28. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35343766 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV Spike-Mediated Cell-Cell Fusion Differ in Their Requirements for Receptor Expression and Proteolytic Activation.J Virol. 2021 Apr 12;95(9):e00002-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00002-21. Print 2021 Apr 12. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33608407 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) in the Pathogenesis of ARDS in COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 22;12:732690. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.732690. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiological Relevance of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 As a Metabolic Linker and Therapeutic Implication of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in COVID-19 and Hypertension.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021 Feb;17(1):132-143. doi: 10.1007/s12015-020-10012-x. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021. PMID: 32748331 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sulforaphane inhibits the expression of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 induced in bronchial epithelial IB3-1 cells by exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein.Phytomedicine. 2021 Jul;87:153583. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153583. Epub 2021 May 4. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34033999 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of N-0385 blocking SARS-CoV-2 to treat COVID-19 based on molecular docking and molecular dynamics.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 18;13:1013911. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1013911. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36329841 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphopenia, Lymphopenia-Induced Proliferation, and Autoimmunity.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 16;22(8):4152. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084152. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33923792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced fetal hematopoiesis in response to symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy.Commun Med (Lond). 2023 Dec 11;3(1):177. doi: 10.1038/s43856-023-00406-6. Commun Med (Lond). 2023. PMID: 38082066 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 mechanisms of cell tropism in various organs considering host factors.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 20;10(4):e26577. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26577. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38420467 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fleming I. Signaling by the angiotensin-converting enzyme. Circ Res. 2006;98(7):887–896. - PubMed
-
- Gheblawi M, Wang K, Viveiros A, Nguyen Q, Zhong JC, Turner AJ, Raizada MK, Grant MB, Oudit GY. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 receptor and regulator of the renin-angiotensin system: Celebrating the 20th anniversary of the discovery of ACE2. Circ Res. 2020;126(10):1456–1474. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kuba K, Imai Y, Rao S, Gao H, Guo F, Guan B, Huan Y, Yang P, Zhang Y, Deng W, Bao L, Zhang B, Liu G, Wang Z, Chappell M, Liu Y, Zheng D, Leibbrandt A, Wada T, Slutsky AS, Liu D, Qin C, Jiang C, Penninger JM. A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury. Nat Med. 2005;11(8):875–879. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

