Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and Neurosurgery Residency Action Plan: An Institutional Experience from the United States
- PMID: 32693224
- PMCID: PMC7368409
- DOI: 10.1016/j.wneu.2020.07.080
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and Neurosurgery Residency Action Plan: An Institutional Experience from the United States
Abstract
Background: The current pandemic crisis, caused by a novel human coronavirus named severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2), has forced a dramatic change in our society. A key portion of the medical work force on the frontline is composed of resident physicians. Thus, it becomes imperative to create an adequate and effective action plan to restructure this valuable human resource amid the SARS-CoV2 pandemic. We sought to describe a comprehensive approach taken by a Neurosurgery Department in quaternary care academic institution in the United States of America amid the SARS-CoV2 pandemic focused in resident training and support.
Objective: To describe a comprehensive approach taken by a Neurosurgery Department in quaternary care academic institution in the United States of America amid the SARS-CoV2 pandemic focused on resident training and support.
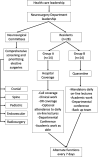
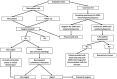
Results: A restructuring of the Neurosurgery Department at our academic institution was performed focused on decreasing their risk of infection/exposure and transmission to others, while minimizing negative consequences in the training experience. An online academic platform was built for resident education, guidance, and support, as well as continue channel for pandemic update by the department leadership.
Conclusions: The SARS-CoV2 pandemic constitutes a global health emergency full of uncertainty. Treatment, scope, duration, and economic burden forced a major restructuring of our medical practice. In this regard, academic institutions must direct efforts to diminish further negative impact in the training and education of the upcoming generation of physicians, including those currently in medical school. Perhaps the only silver lining in this terrible disruption will be greater appreciation of the role of current health care providers and educators, whose contributions to our society are often neglected or unrecognized.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Education; Neurosurgery; Pandemic; SARS-CoV2.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neurosurgery Resident Attrition Rates Defy Trends and Decrease During COVID-19 Pandemic.World Neurosurg. 2023 Nov;179:e374-e379. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2023.08.093. Epub 2023 Aug 28. World Neurosurg. 2023. PMID: 37648202
-
#Neurosurgery: A Temporal and Content Analysis of Academic Neurosurgery on Twitter.World Neurosurg. 2021 Sep;153:e481-e487. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2021.06.150. Epub 2021 Jul 6. World Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 34242826
-
Early Changes to Neurosurgery Resident Training During the COVID-19 Pandemic at a Large U.S. Academic Medical Center.World Neurosurg. 2020 Dec;144:e926-e933. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2020.09.125. Epub 2020 Sep 28. World Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32992058 Free PMC article.
-
Emergency Restructuring of a General Surgery Residency Program During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic: The University of Washington Experience.JAMA Surg. 2020 Jul 1;155(7):624-627. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2020.1219. JAMA Surg. 2020. PMID: 32250417 Review.
-
Human and novel coronavirus infections in children: a review.Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021 Feb;41(1):36-55. doi: 10.1080/20469047.2020.1781356. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021. PMID: 32584199 Review.
Cited by
-
A look at the global impact of COVID-19 pandemic on neurosurgical services and residency training.Sci Afr. 2023 Mar;19:e01504. doi: 10.1016/j.sciaf.2022.e01504. Epub 2022 Dec 14. Sci Afr. 2023. PMID: 36531434 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of COVID-19 pandemic on pediatric neurosurgery practice and training in a developing country.Childs Nerv Syst. 2021 Apr;37(4):1313-1317. doi: 10.1007/s00381-020-04953-4. Epub 2020 Nov 1. Childs Nerv Syst. 2021. PMID: 33130919 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on global neurosurgical education: a systematic review.Neurosurg Rev. 2022 Apr;45(2):1101-1110. doi: 10.1007/s10143-021-01664-5. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Neurosurg Rev. 2022. PMID: 34623526 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Covid-19 on Residency Training in Tertiary Health Institutions in Nigeria: A National Survey.Niger Med J. 2023 Dec 5;63(4):267-274. doi: 10.60787/NMJ-63-4-39. eCollection 2022 Jul-Aug. Niger Med J. 2023. PMID: 38863469 Free PMC article.
-
Letter to the Editor: Impact of COVID-19 on Neurosurgery and Review of the Literature.World Neurosurg. 2021 May;149:300-301. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2021.02.088. World Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 33940690 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

