Distinct conformational states of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
- PMID: 32694201
- PMCID: PMC7464562
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abd4251
Distinct conformational states of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
Abstract
Intervention strategies are urgently needed to control the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic. The trimeric viral spike (S) protein catalyzes fusion between viral and target cell membranes to initiate infection. Here, we report two cryo-electron microscopy structures derived from a preparation of the full-length S protein, representing its prefusion (2.9-angstrom resolution) and postfusion (3.0-angstrom resolution) conformations, respectively. The spontaneous transition to the postfusion state is independent of target cells. The prefusion trimer has three receptor-binding domains clamped down by a segment adjacent to the fusion peptide. The postfusion structure is strategically decorated by N-linked glycans, suggesting possible protective roles against host immune responses and harsh external conditions. These findings advance our understanding of SARS-CoV-2 entry and may guide the development of vaccines and therapeutics.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures
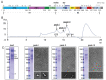


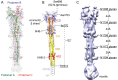

Update of
-
Distinct conformational states of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 May 17:2020.05.16.099317. doi: 10.1101/2020.05.16.099317. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Science. 2020 Sep 25;369(6511):1586-1592. doi: 10.1126/science.abd4251. PMID: 32511405 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Zhong N. S., Zheng B. J., Li Y. M., Poon L. L. M., Xie Z. H., Chan K. H., Li P. H., Tan S. Y., Chang Q., Xie J. P., Liu X. Q., Xu J., Li D. X., Yuen K. Y., Peiris J. S. M., Guan Y., Epidemiology and cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in Guangdong, People’s Republic of China, in February, 2003. Lancet 362, 1353–1358 (2003). 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)14630-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hijawi B., Abdallat M., Sayaydeh A., Alqasrawi S., Haddadin A., Jaarour N., Alsheikh S., Alsanouri T., Novel coronavirus infections in Jordan, April 2012: Epidemiological findings from a retrospective investigation. East. Mediterr. Health J. 19, S12–S18 (2013). 10.26719/2013.19.supp1.S12 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Guan Y., Zheng B. J., He Y. Q., Liu X. L., Zhuang Z. X., Cheung C. L., Luo S. W., Li P. H., Zhang L. J., Guan Y. J., Butt K. M., Wong K. L., Chan K. W., Lim W., Shortridge K. F., Yuen K. Y., Peiris J. S., Poon L. L., Isolation and characterization of viruses related to the SARS coronavirus from animals in southern China. Science 302, 276–278 (2003). 10.1126/science.1087139 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

