Non-invasive early detection of cancer four years before conventional diagnosis using a blood test
- PMID: 32694610
- PMCID: PMC7374162
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-17316-z
Non-invasive early detection of cancer four years before conventional diagnosis using a blood test
Abstract
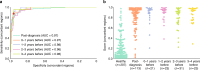
Early detection has the potential to reduce cancer mortality, but an effective screening test must demonstrate asymptomatic cancer detection years before conventional diagnosis in a longitudinal study. In the Taizhou Longitudinal Study (TZL), 123,115 healthy subjects provided plasma samples for long-term storage and were then monitored for cancer occurrence. Here we report the preliminary results of PanSeer, a noninvasive blood test based on circulating tumor DNA methylation, on TZL plasma samples from 605 asymptomatic individuals, 191 of whom were later diagnosed with stomach, esophageal, colorectal, lung or liver cancer within four years of blood draw. We also assay plasma samples from an additional 223 cancer patients, plus 200 primary tumor and normal tissues. We show that PanSeer detects five common types of cancer in 88% (95% CI: 80-93%) of post-diagnosis patients with a specificity of 96% (95% CI: 93-98%), We also demonstrate that PanSeer detects cancer in 95% (95% CI: 89-98%) of asymptomatic individuals who were later diagnosed, though future longitudinal studies are required to confirm this result. These results demonstrate that cancer can be non-invasively detected up to four years before current standard of care.
Conflict of interest statement
J.G., A.G., Q.H., J.M., X.L., L.C., Z.Z., H.N., Z.L., Z.X., H.S., J.D., C.M., and R.L. are employees of Singlera Genomics. Y.G. and R.L. are board members of Singlera Genomics. J.G., A.G., and R.L. are inventors on a patent (US62/657,544) held by Singlera Genomics that covers basic aspects of the library preparation method used in this paper. K.Z. is a co-founder, equity holder, and paid consultant of Singlera Genomics. The terms of these arrangements are being managed by the University of California–San Diego in accordance with its conflict of interest policies. X.C., M.L., Z.Y., X.Y., Y.J., T.Z., C.S., X.Z., M.F., X.W., Y.Y., J.Z., J.W., S.Y., W.Y., and L.J. declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Guide to Early Cancer Diagnosis. (2017)
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68:7–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

