GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Clinical Outcomes to Mechanisms
- PMID: 32694999
- PMCID: PMC7338581
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00967
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Clinical Outcomes to Mechanisms
Abstract
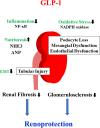
Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD) is the leading cause of end stage renal disease (ESRD) worldwide. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) are now widely used in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D). A series of clinical and experimental studies demonstrated that GLP-1RAs have beneficial effects on DKD, independent of their glucose-lowering abilities, which are mediated by natriuresis, anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative stress properties. Furthermore, GLP-1RAs have been shown to suppress renal fibrosis. Recent clinical trials have demonstrated that GLP-1RAs have beneficial effects on renal outcomes, especially in patients with T2D who are at high risk for CVD. These findings suggest that GLP-1RAs hold great promise in preventing the onset and progression of DKD. However, GLP-1RAs have only been shown to reduce albuminuria, and their ability to reduce progression to ESRD remains to be elucidated. In this review article, we highlight the current understanding of the clinical efficacy and the mechanisms underlying the effects of GLP-1RAs in DKD.
Keywords: GLP-1 receptor agonists; diabetic kidney disease; diabetic nephropathy; dulaglutide; liraglutide; semaglutide.
Copyright © 2020 Kawanami and Takashi.
Figures
References
-
- Bethel M. A., Mentz R. J., Merrill P., Buse J. B., Chan J. C., Goodman S. G., et al. (2020). Microvascular and Cardiovascular Outcomes According to Renal Function in Patients Treated With Once-Weekly Exenatide: Insights From the EXSCEL Trial. Diabetes Care 43, 446–452. 10.2337/dc19-1065 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

