Identification and Functional Analysis of BmNPV-Interacting Proteins From Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera) Larval Midgut Based on Subcellular Protein Levels
- PMID: 32695093
- PMCID: PMC7338592
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01481
Identification and Functional Analysis of BmNPV-Interacting Proteins From Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera) Larval Midgut Based on Subcellular Protein Levels
Abstract
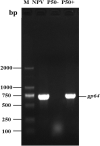
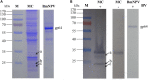
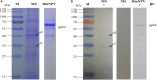
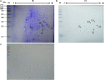
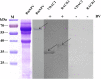
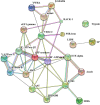
Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus (BmNPV) is a major pathogen causing severe economic loss. However, the molecular mechanism of silkworm resistance to BmNPV and the interactions of this virus with the host during infection remain largely unclear. To explore the virus-binding proteins of silkworms, the midgut subcellular component proteins that may interact with BmNPV were analyzed in vitro based on one- and two-dimensional electrophoresis and far-western blotting combined with mass spectrometry (MS). A total of 24 proteins were determined to be specifically bound to budded viruses (BVs) in two subcellular fractions (mitochondria and microsomes). These proteins were involved in viral transportation, energy metabolism, apoptosis and viral propagation, and they responded to BmNPV infection with different expression profiles in different resistant strains. In particular, almost all the identified proteins were downregulated in the A35 strain following BmNPV infection. Interestingly, there were no virus-binding proteins identified in the cytosolic fraction of the silkworm midgut. Two candidate proteins, RACK1 and VDAC2, interacted with BVs, as determined with far-western blotting and reverse far-western blotting. We speculated that the proteins interacting with the virus could either enhance or inhibit the infection of the virus. The data provide comprehensive useful information for further research on the interaction of the host with BmNPV.
Keywords: BmNPV; BmNPV-interacting proteins; Bombyx mori (B. mori); far-western blotting; subcellular proteins; two-dimensional electrophoresis.
Copyright © 2020 Zhang, Zhu, Yu, You, Wang, Cao, Liu, Wang, Kong, Toufeeq and Xu.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

