Effect of Laryngeal Mask Airway Insertion on Intraocular Pressure Response: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 32695160
- PMCID: PMC7368206
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/7858434
Effect of Laryngeal Mask Airway Insertion on Intraocular Pressure Response: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Use of laryngeal mask airway as an alternative to the endotracheal tube has attracted the attention of several workers with regard to intraocular pressure changes. However, the previous studies have reported different results while comparing intraocular pressure, following insertion of laryngeal mask airway or the endotracheal tube. Therefore, this systematic review and meta-analysis was aimed to generate the best possible evidence on the intraocular pressure response to endotracheal tube intubation and laryngeal mask airway insertion.
Methods: Electronic databases like PubMed, CINAHL, EMBASE, Google Scholar, Cochrane library databases, and Mednar were used. All original peer-reviewed papers which reported the mean and standard deviation of IOP before and after airway instrumentation in both groups were included. Two reviewers independently extracted the data using a standardized data extraction format for eligibility and appraised their quality. Data were analyzed using the STATA version 14 software. The pooled standard mean difference was estimated with the random-effect model. Heterogeneity between studies was assessed by the I 2 statistics test. A subgroup analysis was done to assess the source of variation between the studies.
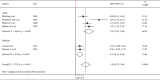
Result: A total of 47 research papers were reviewed, of which, six studies were finally included in this systematic review and meta-analysis. The overall pooled standard mean difference of intraocular pressure was 1.30 (95% CI, 0.70, 1.90), showing that LMA insertion is better than ETT intubation to maintain stable intraocular pressure. A random-effect model was employed to estimate the pooled standard mean differences due to severe heterogeneity (I 2 79.45, p ≤ 0.001).
Conclusion: The available information suggests that the LMA provides lesser intraocular pressure response in comparison with the conventional tracheal tube.
Copyright © 2020 Mohammed Suleiman Obsa et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Puthur B. A comparitive study on cardiovascular response and ease of insertion in classical laryngeal mask airway, proseal laryngeal mask airway and i-gel during surgery under general anaesthesia. Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare. 2015;2(20):3039–3046.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

