Sulphate mineral waters: A medical resource in several disorders
- PMID: 32695648
- PMCID: PMC7365777
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2019.04.004
Sulphate mineral waters: A medical resource in several disorders
Abstract
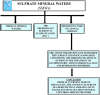
Based on their chemical composition, salus per aquam (spa) mineral waters (or medical mineral waters) can be classified as sulphurous, sulphate, bicarbonate etc. Sulphate mineral waters where the predominant element is sulphate anion SO4 2-, are frequently used in clinical therapy. In this review, we describe and analyze the current scientific knowledge concerning the therapeutic effect of sulphate mineral waters in the treatment of several disorders. Moreover, we underline how important is to integrate spa treatments with other therapeutic approaches to meet the various needs that can arise during a specific pathological state.
Keywords: Chronic disorders; Complementary therapy; Spa medicine; Spa therapy; Sulphate anion.
© 2019 Center for Food and Biomolecules, National Taiwan University. Production and hosting by Elsevier Taiwan LLC.
Figures
References
-
- Queneau P., Boulangé M., Francon A. Ed. Masson; Paris-France: 2000. Médecine Thermale.
-
- Marotta D., Sica C. Composition and classification of Italian mineral waters Nota II. Ann Chim Appl. 1933;23:245–257.
-
- Albertini M.C., Dachà M., Teodori L., Conti M.E. Drinking mineral waters: biochemical effects and health implications - the state of the art. Int J Environ Health. 2007;1(154):153–169.
-
- Casado Á., Ramos P., Rodríguez J., Moreno N., Gil P. vol 55. 2015. Types and Characteristics of Drinking Water for Hydration in the Elderly Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition; pp. 1633–1641. (12) - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources