RSK2 Maintains Adult Estrogen Homeostasis by Inhibiting ERK1/2-Mediated Degradation of Estrogen Receptor Alpha
- PMID: 32697984
- PMCID: PMC7465694
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107931
RSK2 Maintains Adult Estrogen Homeostasis by Inhibiting ERK1/2-Mediated Degradation of Estrogen Receptor Alpha
Abstract
In response to estrogens, estrogen receptor alpha (ERα), a critical regulator of homeostasis, is degraded through the 26S proteasome. However, despite the continued presence of estrogen before menopause, ERα protein levels are maintained. We discovered that ERK1/2-RSK2 activity oscillates during the estrous cycle. In response to high estrogen levels, ERK1/2 is activated and phosphorylates ERα to drive ERα degradation and estrogen-responsive gene expression. Reduction of estrogen levels results in ERK1/2 deactivation. RSK2 maintains redox homeostasis, which prevents sustained ERK1/2 activation. In juveniles, ERK1/2-RSK2 activity is not required. Mammary gland regeneration demonstrates that ERK1/2-RSK2 regulation of ERα is intrinsic to the epithelium. Reduced RSK2 and enrichment in an estrogen-regulated gene signature occur in individuals taking oral contraceptives. RSK2 loss enhances DNA damage, which may account for the elevated breast cancer risk with the use of exogenous estrogens. These findings implicate RSK2 as a critical component for the preservation of estrogen homeostasis.
Keywords: ERK1/2; ERα; MAPK; RSK2; estrogen; growth factors; mammary gland; p90 ribosomal S6 kinase; p90RSK; transgenic mice.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors D.A.L. and G.A.O. have a patent related to this work.
Figures
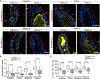
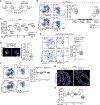
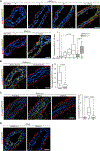
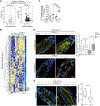
References
-
- Barros RP, and Gustafsson JA (2011). Estrogen receptors and the metabolic network. Cell Metab. 14, 289–299. - PubMed
-
- Blair RM, Fang H, Branham WS, Hass BS, Dial SL, Moland CL, Tong W, Shi L, Perkins R, and Sheehan DM (2000). The estrogen receptor relative binding affinities of 188 natural and xenochemicals: structural diversity of ligands. Toxicol. Sci 54, 138–153. - PubMed
-
- Brill B, Boecher N, Groner B, and Shemanko CS (2008). A sparing procedure to clear the mouse mammary fat pad of epithelial components for transplantation analysis. Lab. Anim 42, 104–110. - PubMed
-
- Brisken C, and Ataca D (2015). Endocrine hormones and local signals during the development of the mouse mammary gland. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol 4, 181–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

