The Functionality of Endothelial-Colony-Forming Cells from Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 32698397
- PMCID: PMC7408543
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9071731
The Functionality of Endothelial-Colony-Forming Cells from Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
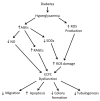
Endothelial-colony-forming cells (ECFCs) are a population of progenitor cells which have demonstrated promising angiogenic potential both in vitro and in vivo. However, ECFCs from diabetic patients have been shown to be dysfunctional compared to ECFCs from healthy donors. Diabetes mellitus itself presents with many vascular co-morbidities and it has been hypothesized that ECFCs may be a potential cell therapy option to promote revascularisation in these disorders. While an allogeneic cell therapy approach would offer the potential of an 'off the shelf' therapeutic product, to date little research has been carried out on umbilical cord-ECFCs in diabetic models. Alternatively, autologous cell therapy using peripheral blood-ECFCs allows the development of a personalised therapeutic approach to medicine; however, autologous diabetic ECFCs are dysfunctional and need to be repaired so they can effectively treat diabetic co-morbidities. Many different groups have modified autologous diabetic ECFCs to improve their function using a variety of methods including pre-treatment with different factors or with genetic modification. While the in vitro and in vivo data from the literature is promising, no ECFC therapy has proceeded to clinical trials to date, indicating that more research is needed for a potential ECFC therapy in the future to treat diabetic complications.
Keywords: cell modification; diabetes; disease-related cell dysfunction; endothelial colony forming cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- D’Avola D., Fernández-Ruiz V., Carmona-Torre F., Méndez M., Pérez-Calvo J., Prósper F., Andreu E., Herrero J.I., Iñarrairaegui M., Fuertes C., et al. Phase 1-2 pilot clinical trial in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis treated with bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells. Transl. Res. 2017;188:80–91.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2016.02.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tanaka R., Masuda H., Kato S., Imagawa K., Kanabuchi K., Nakashioya C., Yoshiba F., Fukui T., Ito R., Kobori M., et al. Autologous G-CSF-Mobilized Peripheral Blood CD34 + Cell Therapy for Diabetic Patients with Chronic Nonhealing Ulcer. Cell Transplant. 2014;23:167–179. doi: 10.3727/096368912X658007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhu J.H., Wang X.X., Zhang F.R., Shang Y.P., Tao Q.M., Zhu J.H., Chen J.Z. Safety and efficacy of autologous endothelial progenitor cells transplantation in children with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension: Open-label pilot study. Pediatr. Transplant. 2008;12:650–655. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3046.2007.00863.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

