Myocardial strain analysis of the right ventricle: comparison of different cardiovascular magnetic resonance and echocardiographic techniques
- PMID: 32698811
- PMCID: PMC7376701
- DOI: 10.1186/s12968-020-00647-7
Myocardial strain analysis of the right ventricle: comparison of different cardiovascular magnetic resonance and echocardiographic techniques
Abstract
Background: Right ventricular (RV) strain is a useful predictor of prognosis in various cardiovascular diseases, including those traditionally believed to impact only the left ventricle. We aimed to determine inter-modality and inter-technique agreement in RV longitudinal strain (LS) measurements between currently available cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) and echocardiographic techniques, as well as their reproducibility and the impact of layer-specific strain measurements.
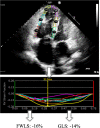
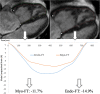
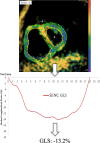
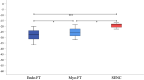
Methods: RV-LS was determined in 62 patients using 2D speckle tracking echocardiography (STE, Epsilon) and two CMR techniques: feature tracking (FT) and strain-encoding (SENC), and in 17 healthy subjects using FT and SENC only. Measurements included global and free-wall LS (GLS, FWLS). Inter-technique agreement was assessed using linear regression and Bland-Altman analysis. Reproducibility was quantified using intraclass correlation (ICC) and coefficients of variation (CoV).
Results: We found similar moderate agreement between both CMR techniques and STE in patients: r = 0.57-0.63 for SENC; r = 0.50-0.62 for FT. The correlation between SENC and STE was better for GLS (r = 0.63) than for FWLS (r = 0.57). Conversely, the correlation between FT and STE was higher for FWLS (r = 0.60-0.62) than GLS (r = 0.50-0.54). FT-midmyocardial strain correlated better with SENC and STE than FT-subendocardial strain. The agreement between SENC and FT was fair (r = 0.36-0.41, bias: - 6.4 to - 10.4%) in the entire study group. All techniques except FT showed excellent reproducibility (ICC: 0.62-0.96, CoV: 0.04-0.30).
Conclusions: We found only moderate inter-modality agreement with STE in RV-LS for both FT and SENC and poor agreement when comparing between the CMR techniques. Different modalities and techniques should not be used interchangeably to determine and monitor RV strain.
Keywords: Cardiovascular magnetic resonance; Right-ventricular function; Speckle-tracking echocardiography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Investigators have received research support (either funding or software support) for other studies from Myocardial Solutions (JE, SK, KK, ARP), Philips (KK, ARP, RML, SK) and Epsilon (RML). SK is on the Advisory Board for Myocardial Solutions.
Figures

References
-
- Plana JC, Galderisi M, Barac A, Ewer MS, Ky B, Scherrer-Crosbie M, et al. Expert consensus for multimodality imaging evaluation of adult patients during and after cancer therapy: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2014;27(9):911–939. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2014.07.012. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

