Discovery and engineering of colchicine alkaloid biosynthesis
- PMID: 32699417
- PMCID: PMC7958869
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2546-8
Discovery and engineering of colchicine alkaloid biosynthesis
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Discovery and engineering of colchicine alkaloid biosynthesis.Nature. 2020 Aug;584(7821):E35. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2606-0. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32728219
Abstract
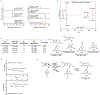
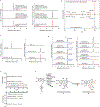
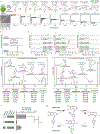
Few complete pathways have been established for the biosynthesis of medicinal compounds from plants. Accordingly, many plant-derived therapeutics are isolated directly from medicinal plants or plant cell culture1. A lead example is colchicine, a US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved treatment for inflammatory disorders that is sourced from Colchicum and Gloriosa species2-5. Here we use a combination of transcriptomics, metabolic logic and pathway reconstitution to elucidate a near-complete biosynthetic pathway to colchicine without prior knowledge of biosynthetic genes, a sequenced genome or genetic tools in the native host. We uncovered eight genes from Gloriosa superba for the biosynthesis of N-formyldemecolcine, a colchicine precursor that contains the characteristic tropolone ring and pharmacophore of colchicine6. Notably, we identified a non-canonical cytochrome P450 that catalyses the remarkable ring expansion reaction that is required to produce the distinct carbon scaffold of colchicine. We further used the newly identified genes to engineer a biosynthetic pathway (comprising 16 enzymes in total) to N-formyldemecolcine in Nicotiana benthamiana starting from the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine. This study establishes a metabolic route to tropolone-containing colchicine alkaloids and provides insights into the unique chemistry that plants use to generate complex, bioactive metabolites from simple amino acids.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures









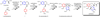



Comment in
-
How the flame lily synthesizes a therapeutic natural product.Nature. 2020 Aug;584(7819):49-50. doi: 10.1038/d41586-020-01675-0. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32699367 No abstract available.
References
-
- Davis MW Colchicine compositions and methods. U.S. Patent No 7,964,647. July 19 (2011).
-
- Jana S & Shekhawat GS Critical review on medicinally potent plant species: Gloriosa superba. Fitoterapia 82, 293–301 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Sivakumar G Upstream biomanufacturing of pharmaceutical colchicine. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol 38, 83–92 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

