Impact of Monthly A1C Values Obtained at Home on Glycemic Control in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 32699471
- PMCID: PMC7364448
- DOI: 10.2337/cd19-0086
Impact of Monthly A1C Values Obtained at Home on Glycemic Control in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
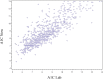
The purpose of this randomized controlled clinical trial was to determine whether an A1C value obtained at home by participants followed by a phone discussion of the result with a clinician would lead to 1) a more rapid and significant decrease in A1C, 2) more effective advancement of diabetes treatment, and 3) improvement in diabetes self-care behaviors. The study included 307 participants with type 2 diabetes, most of whom were of Latino origin. All study participants experienced a statistically significant reduction in mean A1C (control subjects -0.3%, P = 0.04; intervention subjects -0.5%, P = 0.0002), but there was a statistically significant difference in the number of people who achieved a reduction of ≥0.5% by 6 months, favoring the intervention (33.6 vs. 46.7%, P = 0.05).
© 2020 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Diabetes Statistics Report, 2017: Estimates of Diabetes and Its Burden in the United States. Atlanta, GA, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2017
-
- American Diabetes Association 6. Glycemic targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care 2020;43(Suppl. 1):S66–S76 - PubMed
-
- Andary R, Fan W, Wong ND. Control of cardiovascular risk factors among US adults with type 2 diabetes with and without cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol 2019;124:522–527 - PubMed
-
- Cagliero E, Levina EV, Nathan DM. Immediate feedback of HbA1c levels improves glycemic control in type 1 and insulin-treated type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 1999;22:1785–1789 - PubMed