MenB-FHbp Vaccine Protects Against Diverse Meningococcal Strains in Adolescents and Young Adults: Post Hoc Analysis of Two Phase 3 Studies
- PMID: 32700260
- PMCID: PMC7452968
- DOI: 10.1007/s40121-020-00319-0
MenB-FHbp Vaccine Protects Against Diverse Meningococcal Strains in Adolescents and Young Adults: Post Hoc Analysis of Two Phase 3 Studies
Abstract
Introduction: Two phase 3 studies in adolescents and young adults demonstrated that MenB-FHbp, a meningococcal serogroup B (MenB) vaccine, elicits protective immune responses after 2 or 3 doses based on serum bactericidal antibody assays using human complement (hSBA) against 4 primary and 10 additional diverse, vaccine-heterologous MenB test strains. Lower limits of quantitation (LLOQs; titers 1:8 or 1:16; titers ≥ 1:4 correlate with protection) were used to evaluate responses to individual strains and all 4 primary strains combined (composite response). A post hoc analysis evaluated percentages of subjects with protective responses to as many as 8 strains combined (4 primary plus additional strains).
Methods: Immune responses were measured using hSBAs against 4 primary strains in adolescents (n = 1509, MenB-FHbp; n = 898, hepatitis A virus vaccine/saline) and young adults (n = 2480, MenB-FHbp; n = 824, saline) receiving MenB-FHbp or control at 0, 2, and 6 months. Ten additional strains were evaluated in subsets of subjects from approximately 1800 MenB-FHbp recipients across both studies. Percentages of subjects with hSBA titers ≥ LLOQ for different numbers of primary strains or primary plus additional strains combined (7 or 8 strains total per subset) were determined before vaccination, 1 month post-dose 2, and 1 month post-dose 3.
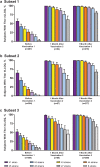
Results: Across the panel of primary plus additional strains, at 1 month post-dose 3, titers ≥ LLOQ were elicited in 93.7-95.7% of adolescents and 91.7-95.0% of young adults for ≥ 5 test strains combined and in 70.5-85.8% of adolescents and 67.5-81.4% of young adults for ≥ 7 strains combined. Among adolescents, 99.8%, 99.0%, 92.8%, and 82.7% had titers ≥ LLOQ against at least 1, 2, 3, and all 4 primary strains, respectively; corresponding percentages for young adults were 99.7%, 97.7%, 94.0%, and 84.5%.
Conclusions: Results support the ability of MenB-FHbp to provide broad coverage against MenB strains expressing diverse FHbp variants.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifiers NCT01830855, NCT01352845.
Keywords: Adolescents; Bactericidal activity; Broad coverage; FHbp; MenB-FHbp vaccine; Meningococcal disease; Meningococcal serogroup B; Neisseria meningitidis; Young adults; hSBA.
Figures



References
-
- Cohn AC, MacNeil JR, Clark TA, et al. Prevention and control of meningococcal disease: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/rr6202a1.htm. Accessed 3 Feb 2020. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Enhanced Meningococcal Disease Surveillance Report, 2018. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/meningococcal/downloads/NCIRD-EMS-Report-2018.pdf. Accessed 7 Jan 2020.
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Surveillance Atlas of Infectious Diseases. Available at: https://ecdc.europa.eu/en/surveillance-atlas-infectious-diseases. Accessed 14 Apr 2020.
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

