Regiodivergent C-H and Decarboxylative C-C Alkylation by Ruthenium Catalysis: ortho versus meta Position-Selectivity
- PMID: 32700444
- PMCID: PMC7589394
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202007144
Regiodivergent C-H and Decarboxylative C-C Alkylation by Ruthenium Catalysis: ortho versus meta Position-Selectivity
Abstract
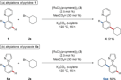
Ruthenium(II)biscarboxylate complexes enabled the selective alkylation of C-H and C-C bonds at the ortho- or meta-position. ortho-C-H Alkylations were achieved with 4-, 5- as well as 6-membered halocycloalkanes. Furthermore, the judicious choice of the directing group allowed for a full control of ortho-/meta-selectivities. Detailed mechanistic studies by experiment and computation were performed and provided strong support for an oxidative addition/reductive elimination process for ortho-alkylations, while a homolytic C-X cleavage was operative for the meta-selective transformations.
Keywords: C−C activation; C−H activation; alkylation; decarboxylation; ruthenium.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures












References
-
- For selected reviews, see:
-
- Rej S., Ano Y., Chatani N., Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 1788–1887; - PubMed
-
- Gandeepan P., Müller T., Zell D., Cera G., Warratz S., Ackermann L., Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 2192–2452; - PubMed
-
- Wang C.-S., Dixneuf P. H., Soulé J.-F., Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 7532–7585; - PubMed
-
- Newton C. G., Wang S.-G., Oliveira C. C., Cramer N., Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8908–8976; - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

