Evaluation of Heat Effects on Fentanyl Transdermal Delivery Systems Using In Vitro Permeation and In Vitro Release Methods
- PMID: 32702372
- PMCID: PMC7644256
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xphs.2020.07.013
Evaluation of Heat Effects on Fentanyl Transdermal Delivery Systems Using In Vitro Permeation and In Vitro Release Methods
Abstract
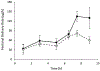
Experimental conditions that could impact the evaluation of heat effects on transdermal delivery systems (TDS) using an in vitro permeation test (IVPT) and in vitro release testing (IVRT) were examined. Fentanyl was the model TDS. IVPT was performed using Franz diffusion cell, heating lamp, and human skin with seven heat application regimens. IVRT setup was similar to IVPT, without using skin. Dissolution study was conducted in a modified dissolution chamber. The activation energy of skin permeation for fentanyl was determined using aqueous solution of fentanyl. In IVPT, the increase of temperature from 32 °C to 42 °C resulted in a 2-fold increase in flux for fentanyl TDS, consistent with the activation energy determined. The magnitude of flux increase was affected by the heat exposure onset time and duration: higher flux was observed when heat was applied earlier or following sustained heat application. Heat induced flux increases could not be observed when inadequate sampling time points were used, suggesting the importance of optimizing sampling time points. Drug release from TDS evaluated using IVRT was fast and the skin was the rate-limiting barrier for TDS fentanyl delivery under elevated temperature.
Keywords: Fentanyl; Heat effect; In vitro drug release testing (IVRT); In vitro permeation test (IVPT); Skin permeation; Transdermal; Transdermal delivery system (TDS); Transport activation energy.
Copyright © 2020 American Pharmacists Association®. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Shomaker TS, Zhang J, Ashburn MA. Assessing the impact of heat on the systemic delivery of fentanyl through the transdermal fentanyl delivery system. Pain Med. 2000;1(3):225–230. - PubMed
-
- Vanakoski J, Sepp T, Sievi E, Lunell E. Exposure to high ambient temperature increases absorption and plasma concentrations of transdermal nicotine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1996;60(3):308–315. - PubMed
-
- Byl NN. The use of ultrasound as an enhancer for transcutaneous drug delivery: phonophoresis. Phys Ther. 1995;75(6):539–553. - PubMed
-
- Knutson K, Krill S, Lambert W, Higuchi W. Physicochemical aspects of transdermal permeation. J Control Release. 1987;6(1):59–74.
-
- Kligman AM. A biological brief on percutaneous absorption. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1983;9(4):521–560.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

