AMPK activation overcomes anti-EGFR antibody resistance induced by KRAS mutation in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 32703218
- PMCID: PMC7376720
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-020-00584-z
AMPK activation overcomes anti-EGFR antibody resistance induced by KRAS mutation in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is associated with resistance to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) antibodies (both acquired and intrinsic), owing to the amplification or mutation of the KRAS oncogene. However, the mechanism underlying this resistance is incompletely understood.
Methods: DLD1 cells with WT (+/-) or KRAS G13D mutant allele were treated with different concentrations of Cetuximab (Cet) or panitumumab (Pab) to study the mechanism underlying the KRAS mutation-induced resistance to anti-EGFR antibodies. The function of AMPK in KRAS mutation-induced resistance to anti-EGFR antibodies in CRC cells, and the regulatory role of Bcl-2 family proteins in DLD1 cells with WT or mutated KRAS upon AMPK activation were investigated. In addition, xenograft tumor models with the nude mouse using DLD1 cells with WT or mutated KRAS were established to examine the effects of AMPK activation on KRAS mutation-mediated anti-EGFR antibody resistance.
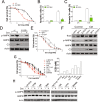
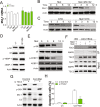
Results: Higher levels of AMPK activity in CRC cells with wild-type KRAS treated with anti-EGFR antibody resulted in apoptosis induction. In contrast, CRC cells with mutated KRAS showed lower AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity and decreased sensitivity to the inhibitory effect of anti-EGFR antibody. CRC cells with mutated KRAS showed high levels of glycolysis and produced an excessive amount of ATP, which suppressed AMPK activation. The knockdown of AMPK expression in CRC cells with WT KRAS produced similar effects to those observed in cells with mutated KRAS and decreased their sensitivity to cetuximab. On the contrary, the activation of AMPK by metformin (Met) or 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR) could overcome the KRAS-induced resistance to the anti-EGFR antibody in vivo and in vitro. The activation of AMPK resulted in the inhibition of myeloid cell leukemia 1 (Mcl-1) translation through the suppression of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway.
Conclusion: The results established herein indicate that targeting AMPK is a potentially promising and effective CRC treatment strategy. Video abstract.
Keywords: AMPK; CRC; EGFR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–249. - PubMed
-
- Chu E. An update on the current and emerging targeted agents in metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2012;11:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Loupakis F, Ruzzo A, Cremolini C, Vincenzi B, Salvatore L, Santini D, Masi G, Stasi I, Canestrari E, Rulli E, et al. KRAS codon 61, 146 and BRAF mutations predict resistance to cetuximab plus irinotecan in KRAS codon 12 and 13 wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2009;101:715–721. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Martini M, Vecchione L, Siena S, Tejpar S, Bardelli A. Targeted therapies: how personal should we go? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011;9:87–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

