Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk Stratification Based on Measurements of Troponin and Coronary Artery Calcium
- PMID: 32703505
- PMCID: PMC7513421
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.05.057
Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk Stratification Based on Measurements of Troponin and Coronary Artery Calcium
Abstract
Background: Low values of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) and coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores of zero are associated with a low risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to evaluate baseline hs-cTnT and CAC in relation to ASCVD.
Methods: Baseline hs-cTnT (limit of detection [LoD] 3 ng/l) and CAC measurements were analyzed across participants age 45 to 84 years without clinical cardiovascular disease from the prospective MESA (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis) in relationship to incident ASCVD.
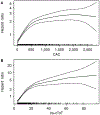
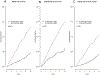
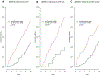
Results: Among 6,749 participants, 1,002 ASCVD events occurred during a median follow-up of 15 years. Participants with detectable CAC (20.1 vs. 5.0 events per 1,000 person-years; adjusted hazard ratio [HR]: 2.35; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.0 to 2.76; p < 0.001) and detectable hs-cTnT (15.4 vs. 5.2 per 1,000 person-years; adjusted HR: 1.47; 95% CI: 1.21 to 1.77; p < 0.001) had higher rates of ASCVD than those with undetectable results. Individuals with undetectable hs-cTnT (32%) had similar risk for ASCVD as did those with a CAC of zero (50%) (5.2 vs. 5.0 per 1,000 person-years). Together, hs-cTnT and CAC (discordance 38%) resulted in the following ASCVD event rates: hs-cTnT < LoD/CAC = 0: 2.8 per 1,000 person-years (reference), hs-cTnT ≥ LoD/CAC = 0: 6.8 per 1,000 person-years (HR: 1.59; 95% CI: 1.17 to 2.16; p = 0.003), hs-cTnT < LoD/CAC > 0: 11.1 per 1,000 person-years (HR: 2.74; 95% CI: 1.96 to 3.83; p < 0.00001), and hs-cTnT ≥ LoD/CAC > 0: 22.6 per 1,000 person-years (HR: 3.50; 95% CI: 2.60 to 4.70; p < 0.00001).
Conclusions: An undetectable hs-cTnT identifies patients with a similar, low risk for ASCVD as those with a CAC score of zero. The increased risk among those with discordant results supports their conjoined use for risk prediction.
Keywords: atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; coronary artery calcium; high-sensitivity cardiac troponin; primary prevention; risk stratification.
Copyright © 2020 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Biomarkers to Establish Low ASCVD Risk: It Takes Two.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Jul 28;76(4):371-373. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.06.002. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32703506 No abstract available.
References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics – 2019 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019; 139: e56–e528. - PubMed
-
- Blaha MJ, Blumenthal RS, Budoff RS, Nasir K. Understanding the utility of zero coronary calcium as a prognostic test: a Bayesian approach. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2011; 4: 253–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201500003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003098/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

