Impaired Renal HCO3- Excretion in Cystic Fibrosis
- PMID: 32703846
- PMCID: PMC7460909
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2020010053
Impaired Renal HCO3- Excretion in Cystic Fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) do not respond with increased urinary HCO3- excretion after stimulation with secretin and often present with metabolic alkalosis.
Methods: By combining RT-PCR, immunohistochemistry, isolated tubule perfusion, in vitro cell studies, and in vivo studies in different mouse models, we elucidated the mechanism of secretin-induced urinary HCO3- excretion. For CF patients and CF mice, we developed a HCO3- drinking test to assess the role of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) in urinary HCO3-excretion and applied it in the patients before and after treatment with the novel CFTR modulator drug, lumacaftor-ivacaftor.
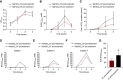
Results: β-Intercalated cells express basolateral secretin receptors and apical CFTR and pendrin. In vivo application of secretin induced a marked urinary alkalization, an effect absent in mice lacking pendrin or CFTR. In perfused cortical collecting ducts, secretin stimulated pendrin-dependent Cl-/HCO3- exchange. In collecting ducts in CFTR knockout mice, baseline pendrin activity was significantly lower and not responsive to secretin. Notably, patients with CF (F508del/F508del) and CF mice showed a greatly attenuated or absent urinary HCO3--excreting ability. In patients, treatment with the CFTR modulator drug lumacaftor-ivacaftor increased the renal ability to excrete HCO3-.
Conclusions: These results define the mechanism of secretin-induced urinary HCO3- excretion, explain metabolic alkalosis in patients with CF, and suggest feasibility of an in vivo human CF urine test to validate drug efficacy.
Keywords: cystic fibrosis; ion transport; kidney tubule; renal tubular acidosis.
Copyright © 2020 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

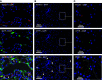

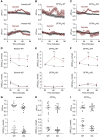

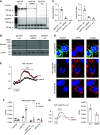

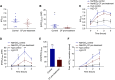

Comment in
-
No Zoom Required: Meeting at the β-Intercalated Cells.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Aug;31(8):1655-1657. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020060844. Epub 2020 Jul 23. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32716314 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Gunnes P, Waldum H, Rasmussen K, Ostensen H, Burhol P: Cardiovascular effects of secretin infusion in man. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 43: 637–642, 1983. - PubMed
-
- Marchand G, Ott C, Lang F, Greger R, Knox F: Effect of secretin on renal blood flow, interstitial pressure, and sodium excretion. Am J Physiol 232: F147–F151, 1977. - PubMed
-
- Bell D, McDermott B: Secretin and vasoactive intestinal peptide are potent stimulants of cellular contraction and accumulation of cyclic AMP in rat ventricular cardiomyocytes. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 23: 959–969, 1994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

