Family-related non-abuse adverse life experiences occurring for adults diagnosed with eating disorders: a systematic review
- PMID: 32704372
- PMCID: PMC7374817
- DOI: 10.1186/s40337-020-00311-6
Family-related non-abuse adverse life experiences occurring for adults diagnosed with eating disorders: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Although previous reviews suggest a strong association between abuse and eating disorders, less is known about non-abuse adverse life experiences, such as parental mental illness or family discord, which occur frequently for this population. The aim of the current study was to identify family-related non-abuse adverse life experiences occurring for adults with eating disorders, and to establish whether they occur for people with anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa or binge-eating disorder more than the general population and other psychiatric populations.
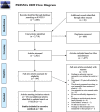
Method: A systematic review of studies focusing on family-related non-abuse adverse life experiences and eating disorders was conducted in accordance with PRISMA guidelines. The search string was applied to four electronic databases including Psycinfo, PubMed/Medline, CINAHL Plus and EMBASE.
Results: Of the 26 studies selected for inclusion, six types of family-related non-abuse adverse life experiences were identified: adverse parenting style; family disharmony; loss of a family member, relative or close person; familial mental health issues; family comments about eating, or shape, weight and appearance; and family disruptions. Findings provided tentative evidence for eating disorder specific (i.e. parental demands and criticism) and non-specific (i.e. familial loss and family disruptions) non-abuse adversities, with findings also suggesting that those with bulimia nervosa and binge-eating disorder were more impacted by loss, family separations and negative parent-child interactions compared to those with anorexia nervosa.
Conclusions: This review provides a clear synthesis of previous findings relating to family-related non-abuse adverse life experiences and eating disorders in adults. Implications for trauma-informed care in clinical practice were discussed (e.g. considering the impact of past life events, understanding the function of ED behaviours, reducing the risk of potential re-traumatisation).
Keywords: Adults; Anorexia nervosa; Binge eating disorders; Bulimia nervosa; Eating disorders; Family adversity; Non-abuse adverse life experiences.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 3. Washington DC: APA press; 1980.
-
- Baumeister RF, Bratslavsky E, Finkenauer C, Vohs KD. Bad is stronger than good. Rev Gen Psychol. 2001;5(4):323.
-
- Boumann CE, Yates WR. Risk factors for bulimia nervosa: a controlled study of parental psychiatric illness and divorce. Addict Behav. 1994;19(6):667–675. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous