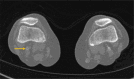
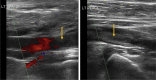
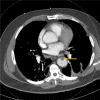
Arterial thromboembolism associated with COVID-19 and elevated D-dimer levels
- PMID: 32704579
- PMCID: PMC7297695
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvscit.2020.06.001
Arterial thromboembolism associated with COVID-19 and elevated D-dimer levels
Abstract
The novel coronavirus 2019 (SARS-CoV-2) was first identified in January 2020 and has since evolved into a pandemic affecting >200 countries. The severity of presentation is variable and carries a mortality between 1% and 3%. We continue to learn about the virus and the resulting acute respiratory illness and hypercoagulability; however, much remains unknown. In our early experience in a high-volume center, we report a series of four cases of acute peripheral artery ischemia in patients with COVID-19 in the setting of elevated D-dimer levels.
Keywords: Arterial thromboembolism; COVID-19; D-dimer.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Rubin E.J., Baden L.R., Morrissey S., Campion E.W. Medical journals and the 2019-nCoV outbreak. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:866. - PubMed
-
- Bunce P.E., High S.M., Nadjafi M., Stanley K., Liles W.C., Christian M.D. Pandemic H1N1 influenza infection and vascular thrombosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52:e14–e17. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous