Effects of liver abscess severity and quality grade on meat tenderness and sensory attributes in commercially finished beef cattle fed without tylosin phosphate
- PMID: 32704655
- PMCID: PMC7205345
- DOI: 10.2527/tas2017.0036
Effects of liver abscess severity and quality grade on meat tenderness and sensory attributes in commercially finished beef cattle fed without tylosin phosphate
Abstract
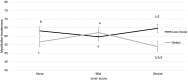
Strip loin steaks (n = 119) were used to evaluate the association between liver abscess severity and USDA quality grade and meat tenderness and sensory attributes of steaks from finished feedlot cattle. Steaks were used in a 3 × 2 factorial treatment structure using a completely randomized design and were collected at a commercial abattoir located in northwest Texas. All cattle were sourced from a single feedlot and fed a common diet that did not include tylosin phosphate. Treatments were USDA quality grades of Select (SEL) and Low Choice (LC) and liver abscess scores of normal (NORM; healthy liver, no abscesses), mild (M; 1 abscess less than 2 cm in diameter to 4 abscesses less than 4 cm in diameter), and severe (SV; 1 abscess greater than 4 cm in diameter or greater than 4 small abscesses). All steak samples were collected on the same day, approximately 36-h post-mortem and were cut from the left side of the carcass at the 13th rib by a trained abattoir employee. Steaks were vacuum-packaged, and aged at 3 ± 1°C for 14-d post-mortem. Warner-Bratzler Shear Force (WBSF) and Slice Shear Force (SSF) analyses were conducted and cook-loss percentage was measured. A trained sensory panel analyzed samples for juiciness, tenderness, and flavor attributes. There were no differences among liver abscess scores for WBSF or SSF (P > 0.52). Warner-Bratzler Shear Force was lower for LC-SV than SEL-SV (P = 0.04). Sensory attributes of initial and sustained juiciness, and overall tenderness were all greater for LC than for SEL steaks (P < 0.04) and connective tissue amount was less for LC steaks when compared to SEL (P = 0.03). Liver abscess score had no effect on any sensory attributes (P > 0.70); however, there was an interaction between quality grade and liver score for myofibillar tenderness (P = 0.03). Within LC steaks, liver abscess score had no effect on myofibrillar tenderness (P > 0.05), however, in SEL steaks, M steaks were more tender than SV steaks (P < 0.03). These results indicate that within quality grades, meat tenderness or sensory attributes were not influenced by liver abscess score but that mild liver abscesses may affect the myofibrillar tenderness of SEL steaks.
Keywords: cattle; feedlot; liver abscesses; meat tenderness; palatability; quality grade.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of feeding zilpaterol hydrochloride to beef and calf-fed Holstein cattle on consumer palatability ratings.J Anim Sci. 2009 Nov;87(11):3712-21. doi: 10.2527/jas.2009-1837. Epub 2009 Aug 28. J Anim Sci. 2009. PMID: 19717772
-
Effectiveness of USDA instrument-based marbling measurements for categorizing beef carcasses according to differences in longissimus muscle sensory attributes.J Anim Sci. 2013 Feb;91(2):1024-34. doi: 10.2527/jas.2012-5514. Epub 2012 Nov 12. J Anim Sci. 2013. PMID: 23148250
-
Beef customer satisfaction: trained sensory panel ratings and Warner-Bratzler shear force values.J Anim Sci. 2003 Jan;81(1):143-9. doi: 10.2527/2003.811143x. J Anim Sci. 2003. PMID: 12597384
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of tenderness metrics in control groups used in comparative nutrition experiments.Transl Anim Sci. 2017 Sep 1;1(3):261-276. doi: 10.2527/tas2017.0031. eCollection 2017 Sep. Transl Anim Sci. 2017. PMID: 32704651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Meta-Analysis of the Effectiveness of High, Medium, and Low Voltage Electrical Stimulation on the Meat Quality of Small Ruminants.Foods. 2020 Nov 2;9(11):1587. doi: 10.3390/foods9111587. Foods. 2020. PMID: 33147731 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic parameter estimates of liver abscesses in feedlot beef cattle.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf029. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf029. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 39910966
-
Initial timing of alfalfa hay supplementation manipulates blood parameters, rumen gene expression, and epithelial microbiota in pre-weaning lambs.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae188. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae188. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39031018 Free PMC article.
-
Short communication: evaluation of an endotoxin challenge and intraruminal bacterial inoculation model to induce liver abscesses in Holstein steers.J Anim Sci. 2023 Jan 3;101:skad242. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad242. J Anim Sci. 2023. PMID: 37480360 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Three New Outer Membrane Adhesion Proteins in Fusobacterium necrophorum.Microorganisms. 2023 Dec 12;11(12):2968. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11122968. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38138112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adhikari K. E., Chambers I. V., Miller R., Vazquez-Araujo L., Bhumiratana N., Philip C.. 2011. Development of a lexicon for beef flavor in intact muscle. J. Sens. Stud. 26:413–420. doi:10.1111/j.1745-459X.2011.00356.x
-
- Amachawadi R. G., Nagaraja T. G.. 2016. Liver Abscesses in cattle: A review of incidence in Holsteins and of bacteriology and vaccine approaches to control in feedlot cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 94:1620–1632. doi:10.2527/jas.2015-0261 - PubMed
-
- American Meat Science Association 2015. Research guidelines for cookery, sensory evaluation, and instrumental tenderness measurements of meat. Am. Meat Sci. Assoc., Champaign, IL.
-
- Acheson R. J., Woerner D. R., Tatum J. D.. 2014. Effects of USDA carcass maturity on sensory attributes of beef produced by grain-finished steers and heifers classified as less than 30 months old using dentition. J. Anim. Sci. 92:1792–1799. doi:10.2527/jas.2013-7553 - PubMed
-
- Brown T. R., Lawrence T. E.. 2010. Association of liver abnormalities with carcass grading performance and value. J. Anim. Sci. 88:4037–4043. doi:10.2527/jas.2010-3219 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
