Alkali addition and roughage inclusion effect on performance and carcass characteristics of feedlot steers fed diets containing 60% dried distillers grains with solubles
- PMID: 32704893
- PMCID: PMC7200494
- DOI: 10.1093/tas/txz121
Alkali addition and roughage inclusion effect on performance and carcass characteristics of feedlot steers fed diets containing 60% dried distillers grains with solubles
Abstract
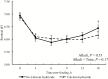
Three experiments were conducted to determine the effectiveness of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) addition and roughage inclusion on digestibility, performance, and carcass characteristics of steers fed 60% dried distillers grains with solubles (DGS). Statistical analyses for studies were conducted using the MIXED procedures of SAS. In experiment 1, 48 steers (353.5 ± 7.55 kg) were allotted to individual pens and fed 1 of 3 diets (dry matter [DM] basis) containing 60% dried DGS, 20% corn silage, and 4% supplement with: 1) 14.5% corn and no Ca(OH)2; 2) 14% corn and 2% Ca(OH)2; and 3) 14.5% additional corn silage and no Ca(OH)2. Steers fed Ca(OH)2 consumed the least (P = 0.03) and steers fed added corn silage consumed the most and had the least gain:feed (P = 0.02). Gain and carcass quality were not affected by treatment (P ≥ 0.48). In experiment 2, 112 steers (375.3 ± 19.25 kg) were allotted to pens (four pens per treatment; seven steers per pen) arranged as a 2 × 2 factorial (roughage × Ca(OH)2) and fed one of four diets (DM basis) containing 60% dried DGS, 17% corn silage, and 4% supplement with: 1) 17.5% corn silage and no Ca(OH)2; 2) 17% corn silage and 2% Ca(OH)2; 3) 17.25% corn stover and no Ca(OH)2; and 4) 17% corn stover and 2% Ca(OH)2. Added stover decreased average daily gain (ADG) compared to added corn silage (P = 0.04). Ca(OH)2 increased ADG when steers were fed stover, but not when steers were fed only corn silage (P = 0.05; interaction). In experiment 3, six ruminally cannulated steers (initial body weight = 352 ± 14.8 kg) were randomly allotted to a 6 × 6 Latin square design to determine the effects of roughage inclusion (corn, corn silage, stover) and Ca(OH)2 addition (0% or 2%) on ruminal characteristics. Feeding stover decreased total volatile fatty acid(s) (VFA) concentration and DM digestibility compared to corn silage or corn (P < 0.01), whereas Ca(OH)2 resulted in greater total VFA concentrations and DM digestibility (P ≤ 0.02). Stover increased rate of DM degradation (K d) and rate of particle outflow from the rumen (P ≤ 0.04) but decreased extent of DM digestion and mean retention time (P ≤ 0.02) compared to corn or silage. Ca(OH)2 increased K d (P < 0.01) and tended to increase (P = 0.06) liquid passage rate. In conclusion, added roughage did not improve performance of cattle fed 60% dried DGS. Ca(OH)2 may decrease intake and maintain performance of cattle fed 60% dried DGS with corn silage as the roughage source and increases ADG when corn stover replaces a portion of the corn silage.
Keywords: calcium hydroxide; cattle; digestibility; kinetics; roughage; rumen pH.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Society of Animal Science.
Figures

References
-
- Aines G. E. 1985. Effects of alkali source and level of treatment of crop residues on fiber composition and digestibility. Ph.D. Dissertation. Lincoln (NE): University of Nebraska.
-
- AOAC 2006. Official methods of analysis. 18th ed.Arlington (VA): Association of Official Analytical Chemist.
-
- Benton J. R., Watson A. K., Erickson G. E., Klopfenstein T. J., Pol K. J., Meyer N. F., and Greenquist M. A.. . 2015. Effects of roughage source and inclusion in beef finishing diets containing corn wet distillers’ grains plus solubles. J. Anim. Sci. 93:4358–4367. doi:10.2527/jas.2015-9211 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blaxter K. L., Graham N. M., and Wainman F. W.. . 1956. Some observations on the digestibility of food by sheep, and on related problems. Br. J. Nutr. 10:69–91. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
