Therapeutic potential of anti-VEGF receptor 2 therapy targeting for M2-tumor-associated macrophages in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 32705303
- PMCID: PMC10991089
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-020-02676-8
Therapeutic potential of anti-VEGF receptor 2 therapy targeting for M2-tumor-associated macrophages in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: Although immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) has become a standard therapeutic strategy in colorectal cancer (CRC) exhibiting microsatellite instability-high, limited patients benefit from this new approach. To increase the efficacy of ICIs in CRC patients, it is crucial to control the function of immunosuppressive cells in the tumor microenvironment. M2-tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are key immunosuppressive cells and promote tumor growth, angiogenesis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. In the present study, we focused on the VEGF signaling pathway in M2-TAMs to control their inhibitory function.
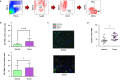
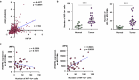
Methods: We evaluated the population of M2-TAMs, the VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2) expression on M2-TAMs, and the correlation between HIF-1α-positive cells and VEGFR2 expression levels on M2-TAMs in CRC using the analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas colorectal adenocarcinoma dataset (n = 592), the flow cytometry of freshly resected surgical specimens of CRC (n = 20), and the immunofluorescence staining of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded whole tissue samples of CRC (n = 20). Furthermore, we performed a functional assay of M2 macrophages through the VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling pathway in vitro.
Results: The population of M2-TAMs and their VEGFR2 expression significantly increased in the tumor compared to the normal mucosa in the CRC patients. HIF1-α-positive cells significantly correlated with the VEGFR2 expression level of M2-TAMs. M2 macrophages induced by cytokines in vitro produced TGF-β1 through the VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling pathway.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that anti-VEGFR2 therapy may have therapeutic potential to control the immune inhibitory functions of M2-TAMs in CRC, resulting in enhanced efficacy of immunotherapy with ICIs.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer (CRC); M2-tumor-associated macrophages (M2-TAMs); TGF-β; VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Cercek A, Roxburgh CSD, Strombom P, Smith JJ, Temple LKF, Nash GM, Guillem JG, Paty PB, Yaeger R, Stadler ZK, Seier K, Gonen M, Segal NH, Reidy DL, Varghese A, Shia J, Vakiani E, Wu AJ, Crane CH, Gollub MJ, Garcia-Aguilar J, Saltz LB, Weiser MR. Adoption of total neoadjuvant therapy for locally advanced rectal cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018 doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.0071. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Overman MJ, Lonardi S, Wong KYM, Lenz HJ, Gelsomino F, Aglietta M, Morse MA, Van Cutsem E, McDermott R, Hill A, Sawyer MB, Hendlisz A, Neyns B, Svrcek M, Moss RA, Ledeine JM, Cao ZA, Kamble S, Kopetz S, Andre T. Durable clinical benefit with nivolumab plus ipilimumab in DNA mismatch repair-deficient/microsatellite instability-high metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(8):773–779. doi: 10.1200/jco.2017.76.9901. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Overman MJ, McDermott R, Leach JL, Lonardi S, Lenz HJ, Morse MA, Desai J, Hill A, Axelson M, Moss RA, Goldberg MV, Cao ZA, Ledeine JM, Maglinte GA, Kopetz S, Andre T. Nivolumab in patients with metastatic DNA mismatch repair-deficient or microsatellite instability-high colorectal cancer (CheckMate 142): an open-label, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(9):1182–1191. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30422-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

