Hydroxychloroquine with or without Azithromycin in Mild-to-Moderate Covid-19
- PMID: 32706953
- PMCID: PMC7397242
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2019014
Hydroxychloroquine with or without Azithromycin in Mild-to-Moderate Covid-19
Erratum in
-
Hydroxychloroquine with or without Azithromycin in Mild-to-Moderate Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 19;383(21):e119. doi: 10.1056/NEJMx200021. Epub 2020 Sep 10. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 33210858 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin have been used to treat patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19). However, evidence on the safety and efficacy of these therapies is limited.
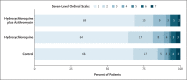
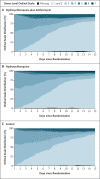
Methods: We conducted a multicenter, randomized, open-label, three-group, controlled trial involving hospitalized patients with suspected or confirmed Covid-19 who were receiving either no supplemental oxygen or a maximum of 4 liters per minute of supplemental oxygen. Patients were randomly assigned in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive standard care, standard care plus hydroxychloroquine at a dose of 400 mg twice daily, or standard care plus hydroxychloroquine at a dose of 400 mg twice daily plus azithromycin at a dose of 500 mg once daily for 7 days. The primary outcome was clinical status at 15 days as assessed with the use of a seven-level ordinal scale (with levels ranging from one to seven and higher scores indicating a worse condition) in the modified intention-to-treat population (patients with a confirmed diagnosis of Covid-19). Safety was also assessed.
Results: A total of 667 patients underwent randomization; 504 patients had confirmed Covid-19 and were included in the modified intention-to-treat analysis. As compared with standard care, the proportional odds of having a higher score on the seven-point ordinal scale at 15 days was not affected by either hydroxychloroquine alone (odds ratio, 1.21; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.69 to 2.11; P = 1.00) or hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin (odds ratio, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.57 to 1.73; P = 1.00). Prolongation of the corrected QT interval and elevation of liver-enzyme levels were more frequent in patients receiving hydroxychloroquine, alone or with azithromycin, than in those who were not receiving either agent.
Conclusions: Among patients hospitalized with mild-to-moderate Covid-19, the use of hydroxychloroquine, alone or with azithromycin, did not improve clinical status at 15 days as compared with standard care. (Funded by the Coalition Covid-19 Brazil and EMS Pharma; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT04322123.).
Copyright © 2020 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Hydroxychloroquine with or without Azithromycin in Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2021 Jan 14;384(2):190. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2031780. Epub 2020 Dec 2. N Engl J Med. 2021. PMID: 33264540 No abstract available.
-
Hydroxychloroquine with or without Azithromycin in Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2021 Jan 14;384(2):190-191. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2031780. Epub 2020 Dec 2. N Engl J Med. 2021. PMID: 33264541 No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard. Geneva: World Health Organization (https://covid19.who.int/).
-
- Cloroquina poderá ser usada em casos graves do coronavírus. Brazil: Ministério da Saúde, May 25, 2020 (https://www.saude.gov.br/noticias/agencia-saude/46601-cloroquina-podera-...).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
