Radiomics for Tumor Characterization in Breast Cancer Patients: A Feasibility Study Comparing Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- PMID: 32708512
- PMCID: PMC7400681
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics10070492
Radiomics for Tumor Characterization in Breast Cancer Patients: A Feasibility Study Comparing Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Abstract
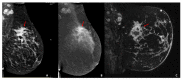
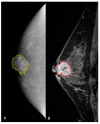
The aim of our intra-individual comparison study was to investigate and compare the potential of radiomics analysis of contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) of the breast for the non-invasive assessment of tumor invasiveness, hormone receptor status, and tumor grade in patients with primary breast cancer. This retrospective study included 48 female patients with 49 biopsy-proven breast cancers who underwent pretreatment breast CEM and MRI. Radiomics analysis was performed by using MaZda software. Radiomics parameters were correlated with tumor histology (invasive vs. non-invasive), hormonal status (HR+ vs. HR-), and grading (low grade G1 + G2 vs. high grade G3). CEM radiomics analysis yielded classification accuracies of up to 92% for invasive vs. non-invasive breast cancers, 95.6% for HR+ vs. HR- breast cancers, and 77.8% for G1 + G2 vs. G3 invasive cancers. MRI radiomics analysis yielded classification accuracies of up to 90% for invasive vs. non-invasive breast cancers, 82.6% for HR+ vs. HR- breast cancers, and 77.8% for G1+G2 vs. G3 cancers. Preliminary results indicate a potential of both radiomics analysis of DCE-MRI and CEM for non-invasive assessment of tumor-invasiveness, hormone receptor status, and tumor grade. CEM may serve as an alternative to MRI if MRI is not available or contraindicated.
Keywords: breast cancer; characterization; contrast-enhanced mammography; diagnosis; magnetic resonance imaging; prognosis; radiomics; texture analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Daly Avendano received travel/accommodations/meeting expenses from BD (BARD) for an interventional masterclass in London. Elizabeth A. Morris has received a grant from GRAIL Inc. for research not related to the present article. Janice S. Sung has received research grants from Hologic and GE. Katja Pinker received payment for activities not related to the present article including lectures and service on speakers’ bureaus and for travel/accommodations/meeting expenses unrelated to activities listed from the European Society of Breast Imaging (MRI educational course, annual scientific meeting), the IDKD 2019 (educational course), and Siemens Healthineers. Maxine S. Jochelson has received an honorarium from GE for speaking and an honorarium for speaking at the Lynn Sage Breast Cancer Symposium and at MD Anderson. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Li H., Zhu Y., Burnside E.S., Huang E., Drukker K., Hoadley K.A., Fan C., Conzen S.D., Zuley M., Net J.M., et al. Quantitative MRI radiomics in the prediction of molecular classifications of breast cancer subtypes in the TCGA/TCIA data set. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2016;2:16012. doi: 10.1038/npjbcancer.2016.12. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

