Comparison of Bioactive Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activities of Different Parts of Taraxacum mongolicum
- PMID: 32708908
- PMCID: PMC7397316
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25143260
Comparison of Bioactive Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activities of Different Parts of Taraxacum mongolicum
Abstract
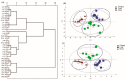
Herbs derived from Taraxacum genus have been used as traditional medicines and food supplements in China for hundreds of years. Taraxacum mongolicum is a famous traditional Chinese medicine derived from Taraxacum genus for the treatment of inflammatory disorders and viral infectious diseases. In the present study, the bioactive phenolic chemical profiles and antioxidant activities of flowers, leaves, and roots of Taraxacum mongolicum were investigated. Firstly, a high performance liquid chromatography method combined with segmental monitoring strategy was employed to simultaneously determine six bioactive phenolic compounds in Taraxacum mongolicum samples. Moreover, multivariate statistical analysis, including hierarchical clustering analysis, principal component analysis, and partial least squares discriminant analysis were performed to compare and discriminate different parts of Taraxacum mongolicum based on the quantitative data. The results showed that three phenolic compounds, caftaric acid, caffeic acid, and luteolin, could be regarded as chemical markers for the differences of flowers, leaves, and roots of Taraxacum mongolicum. In parallel, total phenolic contents, total flavonoid contents and antioxidant activities of different parts of Taraxacum mongolicum were also evaluated and compared. It is clear that Taraxacum mongolicum had antioxidant properties, and the antioxidant capacities of different parts of Taraxacum mongolicum in three antioxidant assays showed a similar tendency: Flowers ≈ leaves > roots, which revealed a positive relationship with their total phenolic and flavonoid contents. Furthermore, to find the potential antioxidant components of Taraxacum mongolicum, the latent relationships of the six bioactive phenolic compounds and antioxidant activities of Taraxacum mongolicum were investigated by Pearson correlation analysis. The results indicated caftaric acid and caffeic acid could be the potential antioxidant ingredients of Taraxacum mongolicum. The present work may facilitate better understanding of differences of bioactive phenolic constituents and antioxidant activities of different parts of Taraxacum mongolicum and provide useful information for utilization of this herbal medicine.
Keywords: Taraxacum mongolicum; antioxidant activity; multivariate statistical analysis; phenolics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Antioxidant Sources from Leaves of Russian Dandelion.Chem Biodivers. 2019 Aug;16(8):e1900250. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201900250. Epub 2019 Jul 18. Chem Biodivers. 2019. PMID: 31250533
-
[Quality evaluation of Taraxaci Herba based on fingerprint analysis and quantitative analysis of multi-components].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018 Sep;43(18):3715-3721. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.2018.0103. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30384538 Chinese.
-
Identification of antioxidants from Taraxacum mongolicum by high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection-radical-scavenging detection-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance experiments.J Chromatogr A. 2008 Oct 31;1209(1-2):145-52. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2008.09.004. Epub 2008 Sep 5. J Chromatogr A. 2008. PMID: 18801488
-
Extraction, purification, structural features, biological activities, modifications, and applications from Taraxacum mongolicum polysaccharides: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Feb;259(Pt 2):129193. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.129193. Epub 2024 Jan 6. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38191106 Review.
-
Ethnobotany of the genus Taraxacum-Phytochemicals and antimicrobial activity.Phytother Res. 2018 Nov;32(11):2131-2145. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6157. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Phytother Res. 2018. PMID: 30039597 Review.
Cited by
-
Carotenoid and Tocopherol Profiling in 18 Korean Traditional Green Leafy Vegetables by LC-SIM-MS.Foods. 2023 Mar 19;12(6):1312. doi: 10.3390/foods12061312. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36981238 Free PMC article.
-
Silver Nanoparticles Formulation of Flower Head's Polyphenols of Cynara scolymus L.: A Promising Candidate against Prostate (PC-3) Cancer Cell Line through Apoptosis Activation.Molecules. 2022 Sep 24;27(19):6304. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196304. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36234842 Free PMC article.
-
Discrimination of Dendropanax morbifera via HPLC fingerprinting and SNP analysis and its impact on obesity by modulating adipogenesis- and thermogenesis-related genes.Front Nutr. 2023 Aug 2;10:1168095. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1168095. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37621738 Free PMC article.
-
NMR Metabolomics of Arctium lappa L., Taraxacum officinale and Melissa officinalis: A Comparison of Spontaneous and Organic Ecotypes.Foods. 2024 May 24;13(11):1642. doi: 10.3390/foods13111642. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38890870 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Compounds from Vegetal Organs of Taraxacum Species (Dandelion) with Biomedical Applications: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 7;26(2):450. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020450. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859166 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sarı A., Keçeci Z. Phenolic compounds from Taraxacum bessarabicum (Hornem.) Hand.-Mazz. subsp. bessarabicum. Planta Med. 2012;78:1225. - PubMed
-
- Mahboubi M. Hepatoprotection by dandelion (Taraxacum officinale) and mechanisms. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2020;10:1–10. doi: 10.4103/2221-1691.273081. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

