Effect of Quercetin on Dexamethasone-Induced C2C12 Skeletal Muscle Cell Injury
- PMID: 32709024
- PMCID: PMC7397304
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25143267
Effect of Quercetin on Dexamethasone-Induced C2C12 Skeletal Muscle Cell Injury
Abstract
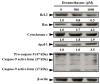
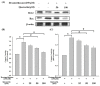
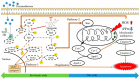
Glucocorticoids are widely used anti-inflammatory drugs in clinical settings. However, they can induce skeletal muscle atrophy by reducing fiber cross-sectional area and myofibrillar protein content. Studies have proven that antioxidants can improve glucocorticoid-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. Quercetin is a potent antioxidant flavonoid widely distributed in fruits and vegetables and has shown protective effects against dexamethasone-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. In this study, we demonstrated that dexamethasone significantly inhibited cell growth and induced cell apoptosis by stimulating hydroxyl free radical production in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. Our results evidenced that quercetin increased C2C12 skeletal cell viability and exerted antiapoptotic effects on dexamethasone-treated C2C12 cells by regulating mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) and reducing oxidative species. Quercetin can protect against dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy by regulating the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio at the protein level and abnormal ΔΨm, which leads to the suppression of apoptosis.
Keywords: C2C12 skeletal muscle cells; antioxidant; apoptosis; dexamethasone; mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm); quercetin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Rhen T., Cidlowski J.A. Antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids--new mechanisms for old drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005;353:1711–1723. - PubMed
-
- Nussinovitch U., de Carvalho J.F., Pereira R.M., Shoenfeld Y. Glucocorticoids and the cardiovascular system: State of the art. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010;16:3574–3585. - PubMed
-
- Zheng Y., Xiong S., Jiang P., Liu R., Liu X., Qian J., Zheng X., Chu Y. Glucocorticoids inhibit lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammatory response by downregulating microRNA-155: A novel anti-inflammation mechanism. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012;52:1307–1317. - PubMed
-
- Rauchhaus U., Schwaiger F.W., Panzner S. Separating therapeutic efficacy from glucocorticoid side-effects in rodent arthritis using novel, liposomal delivery of dexamethasone phosphate: Long-term suppression of arthritis facilitates interval treatment. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009;11:R190. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

