Rationale and design of individualized quality improvement based on the Computer Analysing system to improve Stroke management quality Evaluation (CASE): a multicenter historically controlled study
- PMID: 32709249
- PMCID: PMC7379356
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-020-04598-3
Rationale and design of individualized quality improvement based on the Computer Analysing system to improve Stroke management quality Evaluation (CASE): a multicenter historically controlled study
Abstract
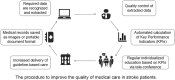
Background: Guideline-based medical care has been identified to improve outcomes in stroke. However, data acquisition and medical quality management during hospital stay still need to be improved in China. We have developed a computer-based medical data collecting system, together with automated calculation of key performance indicators (KPIs) and regular individualized education, and thus aim to explore whether it can improve the medical care quality of acute ischemic stroke (AIS) during hospital stay in stroke centers.
Methods: The individualized quality improvement based on the Computer Analysing system to improve Stroke management quality Evaluation (CASE) trial is a prospective, multicenter, historical control study among 30 stroke centers in China. In this trial, the data is directly extracted from the saved original medical record of each AIS patient during hospital stay, regardless of different Electronic Medical Record System (EMRS) in each center. Then, the automated calculation of KPIs and the regular education via teleconference per month allow the clinicians to examine the causes of non-compliance of guideline-based care and develop programs to decrease their frequency.
Discussion: We compare KPIs between pre-intervention stage and post-intervention stage (without or with education) among stroke centers. If proved effective, this approach might be generalized around China and even worldwide, where a unified EMRS is difficult to be applied and in-patient care needs to be improved.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03684629 . Registered on 9 December 2018. Retrospectively registered.
Keywords: Acute ischemic stroke; Computer-based analyzing system; Key performance indicator; Medical quality improvement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of a Multifaceted Quality Improvement Intervention on Hospital Personnel Adherence to Performance Measures in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke in China: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA. 2018 Jul 17;320(3):245-254. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.8802. JAMA. 2018. PMID: 29959443 Clinical Trial.
-
Trial design and reporting standards for intra-arterial cerebral thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke.Stroke. 2003 Aug;34(8):e109-37. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000082721.62796.09. Epub 2003 Jul 17. Stroke. 2003. PMID: 12869717
-
Rationale and design of a cluster-randomized multifaceted intervention trial to improve stroke care quality in China: The GOLDEN BRIDGE-Acute Ischemic Stroke.Am Heart J. 2015 Jun;169(6):767-774.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2015.03.008. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Am Heart J. 2015. PMID: 26027613 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical review and implications of the guideline for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke.AACN Adv Crit Care. 2014 Apr-Jun;25(2):130-41. doi: 10.1097/NCI.0000000000000017. AACN Adv Crit Care. 2014. PMID: 24752026 Review.
-
Stroke care quality in China: Substantial improvement, and a huge challenge and opportunity.Int J Stroke. 2017 Apr;12(3):229-235. doi: 10.1177/1747493017694392. Epub 2017 Jan 1. Int J Stroke. 2017. PMID: 28381200 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of a Multilevel Program to Improve Clinician Adherence to Management Guidelines for Acute Ischemic Stroke.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 May 2;5(5):e2210596. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.10596. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 35522283 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical