Crosstalk between COVID-19 and prostate cancer
- PMID: 32709978
- PMCID: PMC7378980
- DOI: 10.1038/s41391-020-0262-y
Crosstalk between COVID-19 and prostate cancer
Abstract
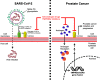
A new coronavirus, named SARS-CoV-2, emerged in Wuhan city, China, in December 2019 causing atypical pneumonia and affecting multiple body organs. The rapidly increasing numbers of infected patients and deaths due to COVID-19 disease necessitated declaring it as a global pandemic. Efforts were combined since then to rapidly develop a treatment and/or a vaccine to combat the deadly virus. Drug repurposing approach has been pursued as a temporary management tactic to treat COVID-19 patients. However, reports about the efficacy of many of the used drugs had been controversial with a dire need to keep the ongoing efforts for rapid development of new treatments. Promising data came out pointing to a possible hidden liaison between prostate cancer (PCa) and COVID-19, where androgen-deprivation therapies (ADT) used in PCa had been shown to instigate a protective role against COVID-19. Delving into the possible mechanisms underlying the crosstalk between COVID-19 and PCa alludes a potential association between SARS-CoV-2 targets on host epithelial cells and PCa genetic aberrations and molecular signatures, including AR and TMPRSS2. The question remains: Can PCa treatments serve as potential therapeutic options for COVID-19 patients?
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. 2020.
-
- Stopsack KH, Mucci LA, Antonarakis ES, Nelson PS, Kantoff PW. TMPRSS2 and COVID-19: serendipity or opportunity for intervention? Cancer Discov. 2020:1–6. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0451. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

