90Y-labeled anti-CD45 antibody allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for high-risk multiple myeloma
- PMID: 32710011
- PMCID: PMC8328580
- DOI: 10.1038/s41409-020-01000-3
90Y-labeled anti-CD45 antibody allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for high-risk multiple myeloma
Abstract
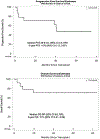
To improve disease control without increasing the toxicity of a reduced-intensity allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) in multiple myeloma (MM), a phase I trial was performed using an antibody-radionuclide conjugate targeting CD45 (90Y-DOTA-BC8) as conditioning. 90Y-DOTA-BC8 was combined with fludarabine and low-dose TBI followed by allogeneic HCT in patients with MM and ≥1 adverse risk characteristic at diagnosis, relapse after autologous transplant, or plasma cell leukemia (PCL). The primary objective was to estimate the maximum tolerated radiation absorbed dose. Fourteen patients were treated (one with PCL, nine failed prior autologous HCT, and nine with ≥1 adverse cytogenetics). Absorbed doses up to 32 Gy to liver were delivered. No dose-limiting toxicities occurred. Non-hematologic toxicities were manageable and included primarily gastrointestinal (43%) and metabolic/electrolyte disturbances (36%). Treatment-related mortality at 100 days was 0%. At a median follow-up of 5 years, the overall survival was 71% (median not reached) and the progression-free survival was 41% (median 40.9 months). The incorporation of CD45-targeted radioimmunotherapy (RIT) into a reduced-intensity allogeneic HCT is well-tolerated and may induce long-term remissions among patients with poor-risk MM, supporting further development of RIT-augmented conditioning regimens for HCT.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01503242.
Figures
References
-
- Palumbo A, Avet-Loiseau H, Oliva S, Lokhorst HM, Goldschmidt H, Rosinol L et al. Revised International Staging System for Multiple Myeloma: A Report From International Myeloma Working Group. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2015; 33(26): 2863–2869. e-pub ahead of print 2015/08/05; doi: 10.1200/jco.2015.61.2267 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Roos-Weil D, Moreau P, Avet-Loiseau H, Golmard J-L, Kuentz M, Vigouroux S et al. Impact of genetic abnormalities after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma: a report of the Société Française de Greffe de Moelle et de Thérapie Cellulaire. Haematologica 2011; 96(10): 1504–1511. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2011.042713 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Crawley C, Iacobelli S, Bjorkstrand B, Apperley JF, Niederwieser D, Gahrton G. Reduced-intensity conditioning for myeloma: lower nonrelapse mortality but higher relapse rates compared with myeloablative conditioning. Blood 2007; 109(8): 3588–3594. e-pub ahead of print 2006/12/13; doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-07-036848 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pagel JM, Gooley TA, Rajendran J, Fisher DR, Wilson WA, Sandmaier BM et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation after conditioning with 131 I–anti-CD45 antibody plus fludarabine and low-dose total body irradiation for elderly patients with advanced acute myeloid leukemia or high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2009; 114(27): 5444–5453. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

