Recommendations and management of hyperglycaemia in pregnancy during COVID-19 pandemic in Italy
- PMID: 32710999
- PMCID: PMC7375279
- DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108345
Recommendations and management of hyperglycaemia in pregnancy during COVID-19 pandemic in Italy
Abstract
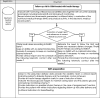
Many specialists use the remote management of people with chronic disease as diabetes, but structured management protocols have not been developed yet. The COVID-19 pandemic has given a big boost to the use of telemedicine, as it allows to maintain the physical distance, essential to the containment of contagion having regular health contact. Encouraging results related to the use of telemedicine in women with hyperglycaemia in pregnancy, have been recently published. It is well known that hyperglycaemia alters the immune response to infections, that inflammation, in turn, worsens glycaemic control and that any form of hyperglycaemia in pregnancy (HIP) has effects not only on the mother but also on development of the foetus. Therefore, the Italian Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Group, together with a group of experts, developed these recommendations in order to guide physicians in the management of HIP, providing specific diagnostic, therapeutic and assistance pathways (PDTAs) for the COVID-19 emergency. Three detailed PDTAs were developed, for type 1, type 2 and gestational diabetes.
Keywords: COVID-19; GDM; Telemedicine; Type 1 diabetes; Type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Stumpfe F.M., Titzmann A., Schneider M.O., Stelzl P., Kehl S., Fasching P.A., et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Pregnancy - a Review of the Current Literature and Possible Impact on Maternal and Neonatal Outcome. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2020;80:380–390. doi: 10.1055/a-1134-5951. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

