Spitz nevus and infliximab: association or coincidence?
- PMID: 32711929
- PMCID: PMC7563016
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abd.2020.01.008
Spitz nevus and infliximab: association or coincidence?
Abstract
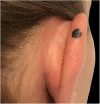
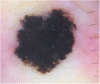
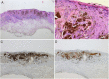
Biological therapies, including anti-TNF agents, are important in the treatment of various chronic inflammatory diseases, including psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease. The increased use of these drugs translates into an increasing awareness of its adverse effects, which include malignancy. In this paper, we describe the case of a 28-year-old woman who developed a spitzoid melanocytic tumor after starting infliximab therapy for ulcerative colitis. The evidence for causality between anti-TNF and melanocytic proliferations is still sparse; nonetheless, treatment-associated immunosuppression seems to play a key role in this phenomenon. Therefore, a regular follow-up with a rigorous skin examination is essential in these patients. Noninvasive techniques such as dermoscopy or reflectance confocal microscopy are particularly useful diagnostic tools in these circumstances.
Keywords: Biological agents; Confocal microscopy; Dermoscopy; Nevus, epithelioid and spindle cell; Skin neoplasms.
Copyright © 2020 Sociedade Brasileira de Dermatologia. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Spitz nevus, Spitz tumor, and spitzoid melanoma: a comprehensive clinicopathologic overview.Dermatol Clin. 2013 Oct;31(4):589-98, viii. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2013.06.012. Dermatol Clin. 2013. PMID: 24075547 Review.
-
Role of In Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy in the Analysis of Melanocytic Lesions.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018 Apr;26(1):64-67. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018. PMID: 29782304 Review.
-
Acral pigmented Spitz nevus in a child with transepidermal migration of melanocytes: Dermoscopic and reflectance confocal microscopic features.Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Mar;35(2):e99-e102. doi: 10.1111/pde.13385. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29314193
-
Appearance of de novo dysplastic spitzoid compound naevus in an adalimumab-treated psoriatic patient: case report and review of the possible causal relationship with TNF-α blockers.Australas J Dermatol. 2014 May;55(2):156-7. doi: 10.1111/ajd.12170. Australas J Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24720429 Review. No abstract available.
-
Dermoscopy of Spitz/Reed naevi and management.G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2019 Aug;154(4):457-465. doi: 10.23736/S0392-0488.19.06294-1. Epub 2019 Feb 14. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2019. PMID: 30762033 Review.
Cited by
-
Nevi, biologics for psoriasis and the risk for skin cancer: A real concern? (Case presentation and short review).Exp Ther Med. 2021 Dec;22(6):1354. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10789. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34659500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fulchiero G.J., Jr, Salvaggio H., Drabick J.J., Staveley-O’Carroll K., Billingsley E.M., Marks J.G. Eruptive latent metastatic melanomas after initiation of antitumor necrosis factor therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56(5 Suppl):S65–7. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y., Friedman M., Liu G., Deodhar A., Chu C.Q. Do tumor necrosis factor inhibitors increase cancer risk in patients with chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disorders? Cytokine. 2018;101:78–88. - PubMed
-
- Katoulis A.C., Kanelleas A., Zambacos G., Panayiotides I., Stavrianeas N.G. Development of two primary malignant melanomas after treatment with adalimumab: a case report and review of the possible link between biological therapy with TNF-alpha antagonists and melanocytic proliferation. Dermatology. 2010;221:9–12. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y., Sun J., Yang Y., Huang Y., Liu G. Malignancy risk of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha blockers: an overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Clin Rheumatol. 2016;35:1–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

