Plexus-specific retinal vascular anatomy and pathologies as seen by projection-resolved optical coherence tomographic angiography
- PMID: 32712135
- PMCID: PMC7855241
- DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100878
Plexus-specific retinal vascular anatomy and pathologies as seen by projection-resolved optical coherence tomographic angiography
Abstract
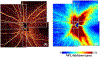
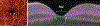
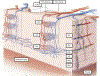
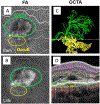
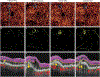
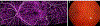
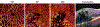
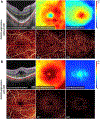
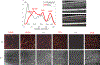
Optical coherence tomographic angiography (OCTA) is a novel technology capable of imaging retinal vasculature three-dimensionally at capillary scale without the need to inject any extrinsic dye contrast. However, projection artifacts cause superficial retinal vascular patterns to be duplicated in deeper layers, thus interfering with the clean visualization of some retinal plexuses and vascular pathologies. Projection-resolved OCTA (PR-OCTA) uses post-processing algorithms to reduce projection artifacts. With PR-OCTA, it is now possible to resolve up to 4 distinct retinal vascular plexuses in the living human eye. The technology also allows us to detect and distinguish between various retinal and optic nerve diseases. For example, optic nerve diseases such as glaucoma primarily reduces the capillary density in the superficial vascular complex, which comprises the nerve fiber layer plexus and the ganglion cell layer plexus. Outer retinal diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa primarily reduce the capillary density in the deep vascular complex, which comprises the intermediate capillary plexus and the deep capillary plexus. Retinal vascular diseases such as diabetic retinopathy and vein occlusion affect all plexuses, but with different patterns of capillary loss and vascular malformations. PR-OCTA is also useful in distinguishing various types of choroidal neovascularization and monitoring their response to anti-angiogenic medications. In retinal angiomatous proliferation and macular telangiectasia type 2, PR-OCTA can trace the pathologic vascular extension into deeper layers as the disease progress through stages. Plexus-specific visualization and measurement of retinal vascular changes are improving our ability to diagnose, stage, monitor, and assess treatment response in a wide variety of optic nerve and retinal diseases. These applications will be further enhanced with the continuing improvement of the speed and resolution of the OCT platforms, as well as the development of software algorithms to reduce artifacts, improve image quality, and make quantitative measurements.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
David Huang, Yali Jia and OHSU have financial interest in Optovue Inc. and Yifan Jian has financial interests in Seymour Vision Inc.
Figures






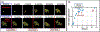


References
-
- Ahmed J, Braun RD, Dunn RJ, Linsenmeier RA, 1993. Oxygen distribution in the macaque retina. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 34, 516–521. - PubMed
-
- Ajtony C, Balla Z, Somoskeoy S, Kovacs B, 2007. Relationship between visual field sensitivity and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness as measured by optical coherence tomography. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 48, 258–263. - PubMed
-
- Al-sheikh M, Sadda SR, Sarraf D, lafe NA, Phasukkijwatana N, Sadda SR, Sarraf D, 2018. Biomarkers of Neovascular Activity in Age-Related Macular Degeneration Using Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography. Retina 0, 1–11. - PubMed
-
- Al-sheikh M, Tepelus TC, Nazikyan T, Sadda SRVR, 2017. Repeatability of automated vessel density measurements using optical coherence tomography angiography. British Journal of Ophthalmology 101, 449–452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

