Corneal Epithelial Findings in Patients with Multiple Myeloma Treated with Antibody-Drug Conjugate Belantamab Mafodotin in the Pivotal, Randomized, DREAMM-2 Study
- PMID: 32712806
- PMCID: PMC7708586
- DOI: 10.1007/s40123-020-00280-8
Corneal Epithelial Findings in Patients with Multiple Myeloma Treated with Antibody-Drug Conjugate Belantamab Mafodotin in the Pivotal, Randomized, DREAMM-2 Study
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Corneal Epithelial Findings in Patients with Multiple Myeloma Treated with Antibody-Drug Conjugate Belantamab Mafodotin in the Pivotal, Randomized, DREAMM-2 Study.Ophthalmol Ther. 2020 Dec;9(4):913-915. doi: 10.1007/s40123-020-00289-z. Ophthalmol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32920777 Free PMC article.
Abstract
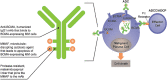
Introduction: Patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) represent an unmet clinical need. Belantamab mafodotin (belamaf; GSK2857916) is a first-in-class antibody-drug conjugate (ADC; or immunoconjugate) that delivers a cytotoxic payload, monomethyl auristatin F (MMAF), to myeloma cells. In the phase II DREAMM-2 study (NCT03525678), single-agent belamaf (2.5 mg/kg) demonstrated clinically meaningful anti-myeloma activity (overall response rate 32%) in patients with heavily pretreated disease. Microcyst-like epithelial changes (MECs) were common, consistent with reports from other MMAF-containing ADCs.
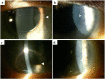
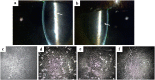
Methods: Corneal examination findings from patients in DREAMM-2 were reviewed, and the clinical descriptions and accompanying images (slit lamp microscopy and in vivo confocal microscopy [IVCM]) of representative events were selected. A literature review on corneal events reported with other ADCs was performed.
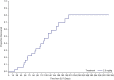
Results: In most patients receiving single-agent belamaf (72%; 68/95), MECs were observed by slit lamp microscopy early in treatment (69% had their first event by dose 4). However, IVCM revealed hyperreflective material. Blurred vision (25%) and dry eye (15%) were commonly reported symptoms. Management of MECs included dose delays (47%)/reductions (25%), with few patients discontinuing due to MECs (1%). The first event resolved in most patients (grade ≥2 MECs and visual acuity [each 77%], blurred vision [67%], and dry eye [86%]), with no reports of permanent vision loss to date. A literature review confirmed that similar MECs were reported with other ADCs; however, event management strategies varied. The pathophysiology of MECs is unclear, though the ADC cytotoxic payload may contribute to on- or off-target effects on corneal epithelial cells.
Conclusion: Single-agent belamaf represents a new treatment option for patients with RRMM. As with other ADCs, MECs were observed and additional research is warranted to determine their pathophysiology. A multidisciplinary approach, involving close collaboration between eye care professionals and hematologist/oncologists, is needed to determine appropriate diagnosis and management of these patients.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier, NCT03525678.
Keywords: Antibody–drug conjugate; Belantamab mafodotin; Cornea; In vivo confocal microscopy; Microcyst-like epithelial changes; Monomethyl auristatin F; Multiple myeloma; Oncology.
Figures


References
-
- Palumbo A, Anderson K. Multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1046–1060. - PubMed
-
- National Cancer Institute. Surveillance, epidemiology, and end results program. cancer stat facts: myeloma; 2020. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/mulmy.html.
-
- Mikhael J. Treatment options for triple-class refractory multiple myeloma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020;20:1–7. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

