Allograft infiltration and meningoencephalitis by SARS-CoV-2 in a pancreas-kidney transplant recipient
- PMID: 32713123
- PMCID: PMC9800697
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.16223
Allograft infiltration and meningoencephalitis by SARS-CoV-2 in a pancreas-kidney transplant recipient
Abstract
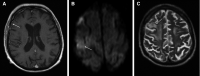
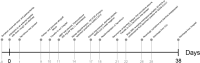
Severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) preferentially affects epithelia of the upper and lower respiratory tract. Thus, impairment of kidney function has been primarily attributed until now to secondary effects such as cytokine release or fluid balance disturbances. We provide evidence that SARS-CoV-2 can directly infiltrate a kidney allograft. A 69-year-old male, who underwent pancreas-kidney transplantation 13 years previously, presented to our hospital with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia and impaired pancreas and kidney allograft function. Kidney biopsy was performed showing tubular damage and an interstitial mononuclear cell infiltrate. Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction from the biopsy specimen was positive for SARS-CoV-2. In-situ hybridization revealed SARS-CoV-2 RNA in tubular cells and the interstitium. Subsequently, he had 2 convulsive seizures. Magnetic resonance tomography suggested meningoencephalitis, which was confirmed by SARS-CoV-2 RNA transcripts in the cerebrospinal fluid. The patient had COVID-19 pneumonia, meningoencephalitis, and nephritis. SARS-CoV-2 binds to its target cells through angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, which is expressed in a broad variety of tissues including the lung, brain, and kidney. SARS-CoV-2 thereby shares features with other human coronaviruses including SARS-CoV that were identified as pathogens beyond the respiratory tract as well. The present case should provide awareness that extrapulmonary symptoms in COVID-19 may be attributable to viral infiltration of diverse organs.
© 2020 The Authors. American Journal of Transplantation published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

